News • bio-hybrid
A microchip to build a first-ever artificial kidney
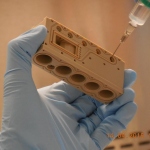
Vanderbilt University Medical Center nephrologist and associate professor of medicine Dr. William H. Fissell IV, is making major progress on a first-of-its kind device to free kidney patients from dialysis. He is building an implantable artificial kidney with microchip filters and living kidney cells that will be powered by a patient’s own heart.