News • mhealth
'Surgery selfies' could spot serious infections early
Smartphone pictures of post-surgical wounds taken by patients and then assessed by clinicians can help with the early identification of infections, a study has found.

Smartphone pictures of post-surgical wounds taken by patients and then assessed by clinicians can help with the early identification of infections, a study has found.
Wound infections are the most common problem after surgery, but promised innovations to tackle the issue do not work and global guidance needs changing.

A research team led by Professor Lim Chwee Teck from the National University of Singapore’s (NUS) Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Health Innovation & Technology (iHealthtech), in collaboration with clinical partners from Singapore General Hospital, has developed a smart wearable sensor that can conduct real-time, point-of-care assessment of chronic wounds wirelessly…

Researchers at RMIT University in Australia have developed smart wound dressings with built-in nanosensors that glow to alert patients when a wound is not healing properly. The multifunctional, antimicrobial dressings feature fluorescent sensors that glow brightly under UV light if infection starts to set in and can be used to monitor healing progress.

Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed a new material that prevents infections in wounds – a specially designed hydrogel, that works against all types of bacteria, including antibiotic-resistant ones. The new material offers great hope for combating a growing global problem. The World Health Organization describes antibiotic-resistant bacteria as one of…
Researchers at Duke University and the University of California, Los Angeles, have developed a biomaterial that significantly reduces scar formation after wounding, leading to more effective skin healing. This new material, which quickly degrades once the wound has closed, demonstrates that activating an adaptive immune response can trigger regenerative wound healing, leaving behind stronger and…
How do cells in our bodies ask for directions? Without any maps to guide them, they still know where to go to heal wounds and renew our bodies. Edouard Hannezo and his group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria) together with Tsuyoshi Hirashima and his group at Kyoto University just published a new study in Nature Physics that shows how mechanical and chemical waves…
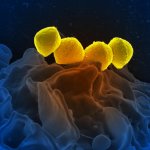
In order to combat bacterial wound infections, Empa researchers have developed cellulose membranes equipped with antimicrobial peptides. Initial results show: The skin-friendly membranes made of plant-based materials kill bacteria very efficiently. If germs invade a wound, they can trigger a long-lasting infection that may fail to heal or even spread throughout the body, leading to…

Imagine a dressing that releases antibiotics on demand and absorbs excessive wound exudate at the same time. Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) hope to achieve just that, by developing a smart coating that actively releases and absorbs multiple fluids, triggered by a radio signal. This material is not only beneficial for the healthcare industry, it is also very promising in…

Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed a new hydrogel based on the body’s natural peptide defense. It has been shown to prevent and treat infections in wounds. The formulation kills multi-resistant bacteria, something that is increasing in importance with antibiotic resistance growing globally. “The ability to effectively heal wounds is key for our survival in evolutionary…
War wounds sustained by frontline soldiers or civilians usually need urgent, specialist, trauma surgery. Over the last two decades much has been learned from injuries sustained during conflicts in, for example, Afghanistan and Iraq. In early June, during a Catastrophe and War Wound key session at the European Wound Management Association conference in Gothenburg, specific remedial approaches to…

Stevens Institute of Technology has signed an exclusive licensing agreement with Bonbouton, giving the company the right to use and further develop a graphene sensing system that detects early signs of foot ulcers before they form, so diabetic patients can access preventative healthcare and manage their health.

Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed a way to 3D print living skin, complete with blood vessels. The advancement, published in Tissue Engineering Part A, is a significant step toward creating grafts that are more like the skin our bodies produce naturally. “Right now, whatever is available as a clinical product is more like a fancy Band-Aid,” said Pankaj Karande, an…

Engineers at the University of Edinburgh have devised a fabric dressing whose thickness and elasticity can be custom-matched to specific areas of the body. The material is able to be absorbed by the skin’s own tissue as it heals. Two synthetic materials are blended to produce nanometre-sized fibres – thousands of times thinner than a hair – which can be fabricated in minutes. Edinburgh…
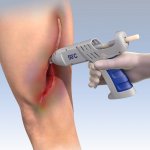
Hot-glue guns can be used for more than putting together cardboard furniture, home decorations, and toys. In fact, researchers at the Technion–Israel Institute of Technology have developed a hot-glue gun to adhere human tissues that have been seriously injured.

Many methods to treat current or chronic wounds are available. However, the differences in general conditions prevailing in hospital, or for out-patient care, make effective therapy more difficult. Each patient also has other preconditions for healing. Improved communication between everyone involved in the treatment would benefit patients. We see a lot of progress with the issue of “wounds”,…
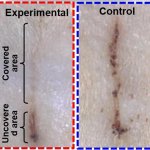
Skin has a remarkable ability to heal itself. But in some cases, wounds heal very slowly or not at all, putting a person at risk for chronic pain, infection and scarring. Now, researchers have developed a self-powered bandage that generates an electric field over an injury, dramatically reducing the healing time for skin wounds in rats. They report their results in ACS Nano. Chronic skin wounds…

Results after suturing are not always aesthetic. Wound treatment with tissue adhesives offer a quick healing process, good tolerance and low scarring. Among these, EPIGLU is an especially fast polymerising product, an Ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate with good closure properties even for injuries that are under tension, Meyer-Haake GmbH Medical Innovations reports: ‘The product, which has been on the…

A UK company that specialises in the development and manufacture of ‘zero pressure’ technology is showing its full range of mattress solutions at Medica this year. Over the last few years, Rober Ltd of Chesterfield, has invested heavily in R&D to develop a complete range of pressure ulcer mattresses that cater for a variety of needs, including patients who are immobile, bariatric or have…

Whilst acknowledging that state-of-the-art bioengineering approaches are being applied in preventing Medical Device Related Pressure Ulcers (MDRPUs), Professor Amit Gefen, from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Tel Aviv University, believes there are gaps in knowledge and technology in this area and therefore more must be done to improve patient care and avoid additional healthcare…
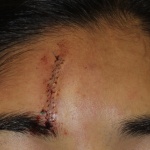
When it comes to the physical scars surgery leaves behind, a new study shows patients and doctors often don’t assess their severity the same way. Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found patients and physicians disagreed in their scar evaluations 28 percent of the time, with patients more likely to focus on the depth of the scar while physicians…
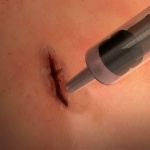
Sutures and staples are the traditional methods for closing surgical incisions and wounds in emergency situations. However, these methods can be inadequate in complex surgeries and cannot make an air-tight or liquid-tight seal on a lung or artery wound or incision. Now researchers funded by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) have created a surgical glue that…

Smith & Nephew, the global medical technology business, announces the European launch of MolecuLight i:X, the easy to use, handheld imaging device that instantly measures wound surface area and visualises the presence and distribution of potentially harmful bacteria in wounds. Currently wound assessments are made with the naked eye which can lack the accuracy required to most effectively…

Princeton researchers have discovered that when water flows around long plastic fibers, the flexible fiber strands tangle like a plate of spaghetti. Instead of a muddled mess, however, this product is in fact a highly useful material known as a hydrogel. Investigated for half a century, hydrogels are increasingly finding uses in areas including artificial tissue engineering, sustained drug…
In a sharp and pointy world, wound healing is a critical and marvelous process. Despite a tremendous amount of scientific study, many outstanding mysteries still surround the way in which cells in living tissue respond to and repair physical damage. One prominent mystery is exactly how wound-healing is triggered: A better understanding of this process is essential for developing new and improved…