News • Neuro-infection
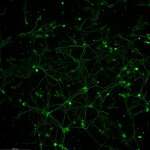
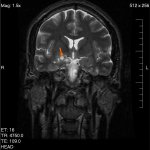
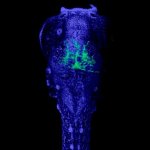
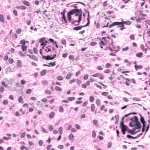
Can Covid-19 infect the brain?
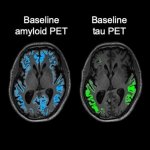
As Covid-19 spreads throughout the country, much attention has been paid to the devastating effects of the virus on the lungs. But doctors are learning how the virus may affect other organs, including the brain. Some patients with Covid-19 have had neurological symptoms, which may include an increased risk of stroke.