News • Betacoronavirus protection
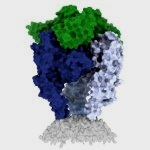
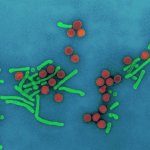
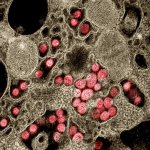
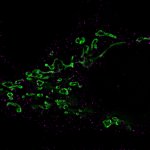
Nanoparticle vaccine protects against Covid-19 variants and related viruses
A new type of vaccine provides protection against a variety of SARS-like betacoronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 variants, in mice and monkeys, according to a new study.