News • Multiple sclerosis
Epstein-Barr virus may be leading cause of MS
A connection between the Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis has long been suspected. A new study provides ‘compelling evidence of causality’.

A connection between the Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis has long been suspected. A new study provides ‘compelling evidence of causality’.
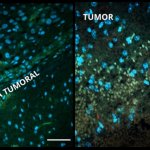
In both the mice and organoids, cytokines suppressed tumor growth after treatment, and defense cells migrated to the brain region affected by the tumor, alerting the immune system to its existence.

Researchers have developed a diagnostic for Sars-CoV-2 that is capable of differentiating between Covid-19 and the garden-variety bug with fast turnaround.
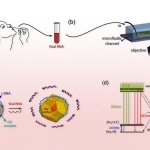
Scientists at have designed a quantum sensor to detect SARS-CoV-2 faster, cheaper, and more accurate than the current gold-standard technique, PCR.
An international team of scientists have identified antibodies that neutralize omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 variants.
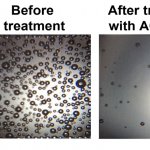
In experiments using saliva samples from COVID-19 patients, the gum, which contains the ACE2 protein, neutralized the virus.

A new rapid molecular diagnostic test from Cepheid has received the CE mark for distribution in the European market. The test, called Xpert Xpress CoV-2/Flu/RSV plus, is designed for qualitative detection of the viruses causing Covid-19, Flu A, Flu B, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections from a single patient sample. The new plus version of the test provides a third gene target for…
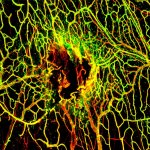
Researchers have found a possible explanation for why some patients recover much more poorly from brain injury if they later become infected.

Study suggests need for better ventilation and tight-fitting masks, in addition to widespread vaccination to help stop spread of the virus.
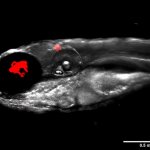
Researchers have found a way to defeat the multi-resistant bacterium Mycobacterium abscessus, a relative of the causes of tuberculosis and leprosy.

To better prepare and protect the world from global disease threats, H.E. German Federal Chancellor Dr Angela Merkel and Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General, have inaugurated the new WHO Hub for Pandemic and Epidemic Intelligence, based in Berlin.
Viruses do not always kill the cells they infect. Researchers at the University of Basel have discovered in experiments with mice that cells have the power to self-heal and eliminate viruses. However, these cells undergo long-term changes. The findings may provide a hint as to why cured hepatitis C patients are more susceptible to liver cancer for years after.
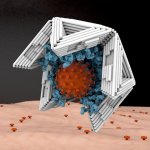
To date, there are no effective antidotes against most virus infections. An interdisciplinary research team at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now developed a new approach: they engulf and neutralize viruses with nano-capsules tailored from genetic material using the DNA origami method. The strategy has already been tested against hepatitis and adeno-associated viruses in cell…
When viruses infect cells, changes in the cell nucleus occur, and these can be observed through fluorescence microscopy. Using fluoresence images from live cells, researchers at the University of Zurich have trained an artificial neural network to reliably recognize cells that are infected by adenoviruses or herpes viruses. The procedure also identifies severe acute infections at an early stage.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation resulting from the inflammatory response to coronavirus infection may be the cause of previously unexplained long Covid symptoms—such as fatigue, brain fog, and rashes—that occur in approximately 30% of patients after recovery from initial Covid-19 infection. The first evidence linking EBV reactivation to long Covid, as well as an analysis of long Covid…

A new project led by University of California San Diego Biological Sciences graduate student Joshua Borin has provided evidence that phages that undergo special evolutionary training increase their capacity to subdue bacteria.
Months after recovering from mild cases of COVID-19, people still have immune cells in their body pumping out antibodies against the virus that causes COVID-19, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such cells could persist for a lifetime, churning out antibodies all the while.

Understanding every step in the life cycle of a virus is crucial for identifying potential targets for treatment. Now, scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria were able to show how a virus from the retrovirus family – the same family as HIV – protects its genetic information and becomes infectious. Furthermore, they show an unexpected flexibility of the virus. This…
Infection with parasitic intestinal worms (helminths) can apparently cause sexually transmitted viral in-fections to be much more severe elsewhere in the body. This is shown by a study led by the Universities of Cape Town and Bonn. According to the study, helminth-infected mice developed significantly more severe symptoms after infection with a genital herpes viruses (Herpes Simplex Virus). The…
Antimicrobial technologies such as coatings and textiles containing silver and copper are helping people during the Covid-19 pandemic by ensuring that whatever they touch, whether that is a door handle or their own mask, is free from live SARS-CoV-2 particles. But how exactly do these antimicrobial technologies work? How can a silver, copper or even polymeric coating kill microorganisms such as…
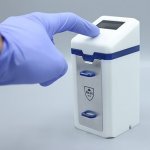
Emerging technologies can screen for cervical cancer better than Pap smears and, if widely used, could save lives both in developing nations and parts of countries, like the United States, where access to health care may be limited. In Biophysics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital write advances in nanotechnology and computer learning are among the…

Using an ordinary light microscope, engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have devised a technique for imaging biological samples with accuracy at the scale of 10 nanometers — which should enable them to image viruses and potentially even single biomolecules, the researchers say. The new technique builds on expansion microscopy, an approach that involves embedding…

Researchers are developing a COVID-19 vaccine that could provide protection against both existing and future strains of the COVID-19 virus, and other coronaviruses, and cost about $1 a dose has shown promising results in early animal testing.

A global group of researchers is calling for better integration of viral genetics, bioinformatics, and public health to enable better pandemic response now and better pandemic preparedness in the future. In a comment piece in the journal Nature, an international collaboration of specialists in viral and genetic analysis, led by Swiss scientists Dr. Emma Hodcroft at the University of Bern and…
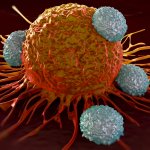
An international research group led by the University of Basel has developed a promising strategy for therapeutic cancer vaccines. Using two different viruses as vehicles, they administered specific tumor components in experiments on mice with cancer in order to stimulate their immune system to attack the tumor. The approach is now being tested in clinical studies.