News • Feline findings
Cats could help in development of anti-HIV drugs
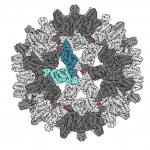
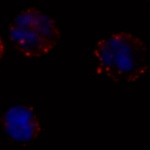
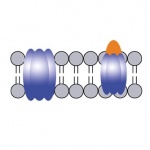
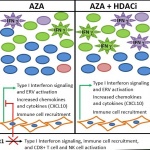
Feline AIDS is caused by the Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV), which is very similar to the HIV-1 virus that affects millions of humans. While FIV does not infect humans, many groups research the virus to benefit cats, and perhaps more importantly, because of its many parallels with the AIDS virus. Despite the use of dedicated drugs, HIV-1 manages to thrive and multiply within the cell and…