Skin repair
Badly sunburned? Vitamin D can help
High doses of vitamin D taken one hour after sunburn significantly reduce skin redness, swelling, and inflammation, according to double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial out of Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center.
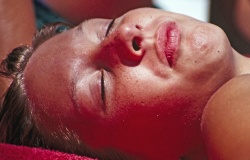
In the study, 20 participants were randomized to receive a placebo pill or 50,000, 100,000, or 200,000 IU of vitamin D one hour after a small UV lamp “sunburn” on their inner arm. Researchers followed up with the participants 24, 48, 72 hours and 1 week after the experiment and collected skin biopsies for further testing. Participants who consumed the highest doses of vitamin D had long-lasting benefits—including less skin inflammation 48 hours after the burn. Participants with the highest blood levels of vitamin D also had less skin redness and a jump in gene activity related to skin barrier repair.
Benefits depend on dosage
“We found benefits from vitamin D were dose-dependent,” said Kurt Lu, MD, senior author on the study and Assistant Professor of Dermatology at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center. “We hypothesize that vitamin D helps promote protective barriers in the skin by rapidly reducing inflammation. What we did not expect was that at a certain dose, vitamin D not only was capable of suppressing inflammation, it was also activating skin repair genes.”
The trial is the first to describe acute anti-inflammatory benefits from taking vitamin D. According to the authors, despite widespread attention given to vitamin D deficiency, “there is a lack of evidence demonstrating that intervention with vitamin D is capable of resolving acute inflammation.” By measuring gene activity in the biopsies, the researchers also uncovered a potential mechanism behind how vitamin D aids skin repair. The results suggest vitamin D increases skin levels of an anti-inflammatory enzyme, arginase-1. The enzyme enhances tissue repair after damage and helps activate other anti-inflammatory proteins.
Doses far beyond daily allowances
The study may have people flocking to vitamin supplement aisles, but Lu stresses that the trial tested very high doses of vitamin D that far exceed daily allowances. The Food and Drug Administration’s recommended adult daily allowance for vitamin D is 400 IU. Said Lu, “I would not recommend at this moment that people start taking vitamin D after sunburn based on this study alone. But, the results are promising and worthy of further study.” Lu and colleagues are planning additional studies that could inform treatment plans for burn patients.
Source: Case Western Reserve University
08.07.2017