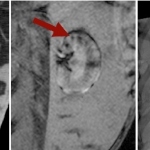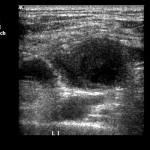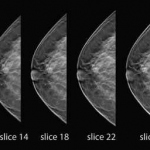
What´s new in breast MRI, tomosynthesis and elastography?
MRI: Although an area of constant debate, this is becoming a widely accepted clinical modality in Europe. However, researchers in The Netherlands have shown that performing pre-operative breast MRI in all women with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) can reduce the need for re-excision.