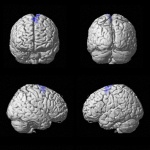
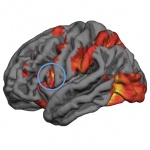
News • Talent, magic, or a bit of both?
The science behind Michael Jackson’s dance moves
When was the last time you watched a Michael Jackson music video? If your answer is “never” or “not for quite a while,” you are really missing a treat. According to Rolling Stone, “No single artist … shaped, innovated or defined the medium of ‘music video’ more than Michael Jackson.” Back in the 1980s and early 1990s, MTV had only one format—music videos—and that genre…