News • Perception research
Why do we see colors the way we do?
Dr. Wolf M. Harmening from University Eye Hospital Bonn, together with American colleagues, studied color vision by probing individual sensory cells – photoreceptors – in the human eye. The results reveal that proximity effects play a key role in how we perceive colors.
Color allows spatial detail to become apparent that has proven vital for survival over the course of evolution
Wolf M. Harmening
A new observation is that proximity effects play a key role: sensitivity of tested photoreceptors varied depending on which cell classes were located in their immediate neighborhood. The results have now been published in advance online and will soon be published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
It is a constant ‘aha’ effect: when the light is switched on in a dark room, color vision sets in. “This not only makes the world more colorful,” says Dr. Wolf M. Harmening, who heads an Emmy Noether research group at Bonn University Eye Hospital. “Color also allows spatial detail to become apparent that has proven vital for survival over the course of evolution.” Some predator camouflage can only be identified through color. Poisonous animals and plants also provide warning signals through color. That human color vision emerges from three independent channels within the retina is well established in the vision science literature. By stimulating individual photoreceptor cells in living subjects, the lead authors Dr. Wolf M. Harmening from University Eye Hospital Bonn and Dr. William S. Tuten from the University of California, Berkeley, together with colleagues from the US universities in Seattle, Washington and Birmingham, Alabama, have now shown on a cellular scale how the human retina conveys color signals.
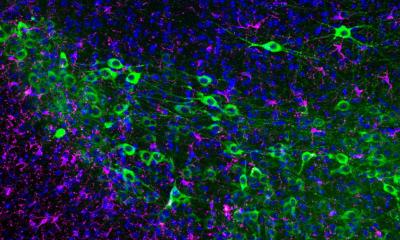
To do this, the researchers used an ophthalmoscope that can examine and stimulate the human retina non-invasively. The novel method – Adaptive Optics Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy – employs a combination of a laser and a very high-resolution microscope, which can even map individual sensory cells in the retina. The research team has now used this ophthalmoscope to study vision in the retinas of two human subjects. According to common theory, all color stimuli can be formed by mixing the primary colors red, green, and blue. While rod photoreceptors are specialized for seeing in the dark, cone photoreceptors convey color vision. They carry light sensitive pigments specialized to absorb wavelengths near the primary colors, the basis of trichromatic vision.
Mapping of the retina
The researchers initially mapped the cone mosaic on the subjects’ retinas by measuring light absorption for certain wavelengths in each photoreceptor. In this way, they were able to determine the sensory cells’ identity, or class, within the framework of trichromacy. By reducing the intensity of the stimulation light, the researchers were then able to determine a detection threshold in each cone, at which light was just barely seen by the subjects. “This is important because we could use the sensitivity of each cell to determine how overall perception is governed by the contribution of individual cones,” reports Harmening.
Most notably, the sensitivity of single cells also depended on the immediate neighboring cells. “If a cone sensitive to red light is surrounded by cells that are more sensitive to green, this cone is more likely to behave like a green cone,” summarizes Harmening. Studying visual processing of color is complex, in part because the brain does not receive raw data from individual photoreceptors but rather an already preprocessed retinal signal. Harmening: “Spatial and color information of individual cones is modulated in the complex network of the retina, with lateral information spreading through what are known as horizontal cells.”
Their finding supports previous assumptions about color vision. “What’s new is that we can now study vision on the most elementary level, cell-by-cell,” says the scientist. Conventional tests of vision use stimuli that necessarily activate hundreds to thousands photoreceptor cells at the same time. Harmening emphasizes that cellular-scale retinal computation such as the proximity effect has important implications, for basic and clinical research. “When the basis of vision is understood better, we open avenues for new diagnoses and treatments in case of retinal disease,” says Harmening. The novel single cell approach offers access to new findings in ophthalmology.
Source: Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn
07.09.2017