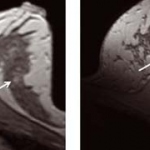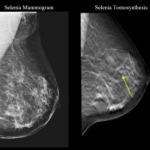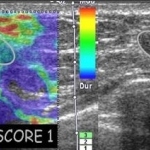
Realtime-Sonoelastography to detect and characterize breast lesions
New possibilities in breast ultrasound comprise techniques for optimizing image quality such as tissue harmonic imaging (THI) and frequency compounding (FC), tools for post-processing US raw data such as strain imaging (elastography), and the use of Realtime-Sonoelastography, PD Dr. Anke Thomas from the Charité in Berlin, Germany, introduced her speech at the Hitachi Symposium Realtime Tissue…