News • Mengla filovirus
Researchers discover Ebola-related virus carried by bats
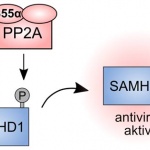
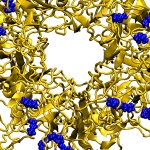
Researchers from Singapore’s Duke-NUS Medical School, in collaboration with scientists in China, have identified and characterised a new genus of filovirus from a Rousettus bat in China. Their findings were published in the journal Nature Microbiology. Bat-borne viruses around the world pose a threat to human and animal health. Filoviruses, especially Ebola virus and Marburg virus, are…