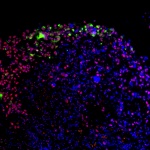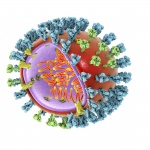
News • Nanovaccine
The flu shot of the future might look like this
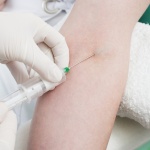
For many of us, a flu shot is a fall routine. Roll up a sleeve, take a needle to the upper arm and hope this year’s vaccine matches whichever viruses circulate through the winter. The most common method to make that vaccine is now more than 70 years old. It requires growing viruses in special, pathogen-free chicken eggs. It’s not a quick and easy manufacturing process. And, at best, it…