Article • Frontline medical advances
Virology is now a key discipline
Virology is fast emerging as a key discipline within modern healthcare against a backdrop of a shifting global demographic and the impact of climate change.

Virology is fast emerging as a key discipline within modern healthcare against a backdrop of a shifting global demographic and the impact of climate change.
Scientists at the University of Basel discovered a fundamental new mechanism explaining the inadequate immune defense against chronic viral infection. These results may open up new avenues for vaccine development.
For the first time, scientists know what happens to a virus’ shape when it invades a host cell, thanks to an experiment by researchers at Penn State College of Medicine and University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. Understanding how the virus shape specifically changes could lead to more effective anti-viral therapies.
Researchers have found that Zika virus can live in eyes and have identified genetic material from the virus in tears, according to a study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The research, in mice, helps explain why some Zika patients develop eye disease, including a condition known as uveitis that can lead to permanent vision loss.
There are a couple strains of herpes so common that researchers estimate 90% of the human population have them. These strains, human herpes 6 and human herpes 7, usually do not cause severe symptoms when people acquire them. But researchers know that under certain circumstances, dormant herpes viruses in the body can unexpectedly come roaring back and cause complications not typically associated…
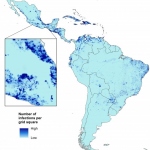
Research by scientists in the US and UK has estimated that up to 1.65 million childbearing women in Central and South America could become infected by the Zika virus by the end of the first wave of the epidemic. Researchers from the WorldPop Project and Flowminder Foundation at the University of Southampton and colleagues from the University of Notre Dame and University of Oxford have also found…
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified antibodies capable of protecting against Zika virus infection, a significant step toward developing a vaccine, better diagnostic tests and possibly new antibody-based therapies. The work, in mice, helps clarify recent research that also identified protective Zika antibodies but lacked important details on how the…

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc. (Siemens) an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for its real-time PCR Zika Virus assay, the VERSANT® Zika RNA 1.0 Assay (kPCR) Kit. With respect to Zika in vitro diagnostic tests, FDA has been authorized to issue EUAs to allow for use of unapproved medical products or unapproved uses of approved medical…

Researchers from the University of Cambridge and the University of Bath, and The BMJ, show how NHS England, unable to budget for broad access to these drugs, tried to alter the outcome of the NICE process, and when it failed, defied NICE’s authority by rationing access to them.

Researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) have uncovered a potential genetic trigger of systemic autoimmune disease. The study, the culmination of more than 10 years of research, discovered virus-like elements within the human genome linked to the development of two autoimmune diseases: lupus and Sjogren's syndrome.
First the good news: the most severe Ebola outbreak ever has been contained. Last December, Guinea, where the first infection was reported in late 2013, was declared free of Ebola cases. Liberia was considered free of Ebola in mid-January after no new case had been reported for 42 days (the WHO criterion for ‘free of Ebola’).
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes hepatitis B, an infectious disease that afflicts 230 million people worldwide, thereof 440 000 in Germany. Persistence of the virus in liver cells leads to progressive organ damage in the patient and contributes to a high risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer development. Providing a new paradigm to hepatitis B understanding, researchers at the German Cancer Research…

The Zika epidemic has long assumed global proportions, experts told the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology in Copenhagen. Europe needs to get prepared to deal with the relentless spread of the health threat, in particular with a view to “imported” infection. Awareness for prevention and personal protection is important, in particular with thousands of athletes and fans soon…

The President of the World Federation of Neurology (WFN) Prof Raad Shakir (London), said today that following the first confirmed Zika-related case of microcephaly on US territory, in Puerto Rico, and the ever-growing number of sexually-transmitted Zika infections in Europe, “it is increasingly obvious that the Zika epidemic has long assumed global proportions.” As the opening of the Olympics…

Virologists from KU Leuven, Belgium, have shown that an experimental antiviral drug against hepatitis C slows down the development of Zika in mice. The research team was led by Professor Johan Neyts from the Laboratory of Virology and Chemotherapy.
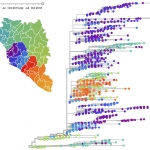
In recent years, we have witnessed multiple epidemics of viral diseases such as Ebola or Zika. Rapid targeted intervention is key to containment. Real-time data integration and analysis can help public health authorities to maximize efficacy of intervention strategies. Dr. Richard Neher from the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, Germany and Dr. Trevor Bedford from the Fred…

As one of medicine’s largest challenges, viral infections often escape vaccines due to their natural ability to mutate rapidly and develop drug resistance easily. Many viruses, such as Zika, Ebola and dengue fever, have grown into major global health epidemics with great human and economic toll. IBM Research and Singapore’s Institute of Bioengineering, Nanotechnology (IBN) announced they have…

As scientists scramble to get a Zika virus vaccine into human trials by the end of the summer, a team of researchers is working on the first-ever vaccine to prevent another insect-borne disease – Leishmaniasis – from gaining a similar foothold in the Americas.

No self-respecting TV crime series is without a pathologist – but the fictitious pathologist who incessantly solves crimes has little to do with reality.
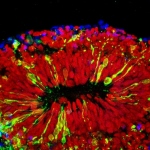
Studying a new type of pinhead-size, lab-grown brain made with technology first suggested by three high school students, Johns Hopkins researchers have confirmed a key way in which Zika virus causes microcephaly and other damage in fetal brains: by infecting specialized stem cells that build its outer layer, the cortex.
Before his presentation at ECCMID 2016, Dr Guillaume Béraud, Infectious Disease Specialist, in the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Poitiers, Poitiers, France, talked to European Hospital about the results from his modelling of these three “childhood” diseases measles, mumps and rubella.
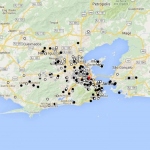
Since the recent link to severe neurological defects in infants born to mothers infected during pregnancy, Zika virus (ZIKV) has become a public health and research priority. A study reports details from the 2015 Zika outbreak in Rio de Janeiro - the first with a high proportion of cases confirmed by molecular diagnosis - and proposes changes to the current diagnostic criteria for ZIKV disease.
The Zika virus may be associated with an autoimmune disorder that attacks the brain's myelin similar to multiple sclerosis, according to a small study that is being released today and will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 68th Annual Meeting in Vancouver, Canada, April 15 to 21, 2016.

The European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Disease (ESCMID) – an organization that explores risks, knowledge sharing and best practices in the fight against infectious disease – has received more than 300 late-breaker abstract submissions for its annual congress, ECCMID 2016 in Amsterdam.

Rapid testing for the Zika virus is a critical need in the recent Ebola-affected countries of Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea, says a Georgetown University professor, because of the recent Zika outbreak on nearby Cape Verde and the similarity in symptoms between Zika and early Ebola.