News • Combined with antibiotics
Bacteria-killing viruses to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria
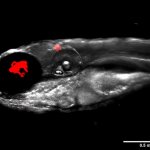
Researchers have found a way to defeat the multi-resistant bacterium Mycobacterium abscessus, a relative of the causes of tuberculosis and leprosy.

Researchers have found a way to defeat the multi-resistant bacterium Mycobacterium abscessus, a relative of the causes of tuberculosis and leprosy.
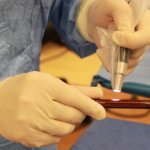
Customizable to individual patients and requiring less than 10 minutes to prepare and use, new surgical implant coating prevented 100% of infections in mice.
Hospitalized Covid-19 patients are substantially more likely to harbor autoantibodies — antibodies directed at their own tissues or at substances their immune cells secrete into the blood — than people without Covid-19, according to a new study.
Colourful, 3D rendered scientific images are fascinating - but can they deceive viewers? New research from Spain suggests this might be the case. According to the study by the Instituto de Radio Televisión Española and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona conducted during the Covid-19 lockdown, black and white images of SARS-CoV-2 make the virus seem more infectious. The results, published on…

To better prepare and protect the world from global disease threats, H.E. German Federal Chancellor Dr Angela Merkel and Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General, have inaugurated the new WHO Hub for Pandemic and Epidemic Intelligence, based in Berlin.
Covid-19 infection does not appear to affect the lung function of young adults, according to new research presented at the ‘virtual’ European Respiratory Society International Congress. In the first study to investigate the impact of Covid-19 infection on lung function, researchers led by Dr Ida Mogensen, a post-doctoral fellow at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, found that even…
The World Health Organization (WHO) has taken a closer look at coronavirus variant B.1.621. The strain, first encountered in January 2021 in Colombia, shows traits that could enable the virus to circumvent immune response to vaccination. As a result, the variant, named "Mu", has been classified as "Variant of Interest" (VOI). Despite its prominence in Colombian new infection,…

Each wave of the pandemic has underscored just how contagious Covid-19 is, but there is less clarity among experts on exactly when—and to what extent—infected individuals are most likely to spread the virus.
Viruses do not always kill the cells they infect. Researchers at the University of Basel have discovered in experiments with mice that cells have the power to self-heal and eliminate viruses. However, these cells undergo long-term changes. The findings may provide a hint as to why cured hepatitis C patients are more susceptible to liver cancer for years after.

How long do coronaviruses remain infectious on banknotes and coins? Is it possible to become infected through contact with cash? Experts at the European Central Bank, in collaboration with the Department of Medical and Molecular Virology at Ruhr-Universität Bochum, wanted to clarify this question. The researchers led by Professor Eike Steinmann and Dr. Daniel Todt developed a method specifically…

Antibiotics have been at the heart of modern healthcare since the 1950s. They are prescribed prior to an operation to minimise the risk of infection after the operation. Or antibiotics are prescribed to fight an infection. This practice, which might seem straightforward at first glance, has proven to cause a number of problems itself: Over the last twenty years, it has become increasingly clear…
Researchers have identified a way to improve the immune response in the face of severe viral infections. It is widely known that severe viral infections and cancer cause impairments to the immune system, including to T cells, a process called immune ‘exhaustion’. Overcoming immune exhaustion is a major goal for the development of new therapies for cancer or severe viral infections.
Rapid tests effectively broke Covid-19 infection chains in spring 2021. This is shown by a model developed by researchers of the ECONtribute: Markets & Public Policy Cluster of Excellence of the Universities of Bonn and Cologne, the Collaborative Research Center Transregio 224 EPoS of the Universities of Bonn and Mannheim, and the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA). According to the…
Blood cultures are important laboratory tests to diagnose serious infections. Contamination is a constant concern – a patient could be misdiagnosed due to a false-positive test. Initial specimen diversion (ISD) could radically change this.
When viruses infect cells, changes in the cell nucleus occur, and these can be observed through fluorescence microscopy. Using fluoresence images from live cells, researchers at the University of Zurich have trained an artificial neural network to reliably recognize cells that are infected by adenoviruses or herpes viruses. The procedure also identifies severe acute infections at an early stage.

The idea of visiting the doctor’s office with symptoms of an illness and leaving with a scientifically confirmed diagnosis is much closer to reality because of new technology developed by researchers at McMaster University. Engineering, biochemistry and medical researchers from across campus have combined their skills to create a hand-held rapid test for bacterial infections that can produce…
Higher levels of vaccination against COVID-19 were associated with lower rates of infection with SARS-CoV-2 among a group of unvaccinated people of 16 years of age and under.

New studies demonstrate benefits of dual antibiotic-loaded bone cement (COPAL G+C) to reduce periprosthetic joint infections in risk for infection patients.
Months after recovering from mild cases of COVID-19, people still have immune cells in their body pumping out antibodies against the virus that causes COVID-19, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such cells could persist for a lifetime, churning out antibodies all the while.

Understanding every step in the life cycle of a virus is crucial for identifying potential targets for treatment. Now, scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria were able to show how a virus from the retrovirus family – the same family as HIV – protects its genetic information and becomes infectious. Furthermore, they show an unexpected flexibility of the virus. This…

A study of healthcare workers shows they were three times more likely to become infected during the Covid-19 pandemic compared to the general population. Around one in five of workers who were infected were asymptomatic and unaware they had Covid-19. The study published in ERJ Open Research also shows that it was not only frontline staff who faced the higher risk, suggesting that there was…
A major study from the Washington University School of Medicine details numerous long-term effects of COVID-19, pointing to massive health burden.

What happens when patients can no longer breathe on their own and need to be supported by machines? How far does infected air spread throughout a room? And what safety precautions do medical and nursing staff need to take? Respiratory specialists Dr. Dominic Dellweg and Dr. Jens Kerl together with Dr.-Ing. Conrad Völker, Amayu Wakoya Gena, and Dr. Hayder Alsaad from the Department of Building…
Infection with parasitic intestinal worms (helminths) can apparently cause sexually transmitted viral in-fections to be much more severe elsewhere in the body. This is shown by a study led by the Universities of Cape Town and Bonn. According to the study, helminth-infected mice developed significantly more severe symptoms after infection with a genital herpes viruses (Herpes Simplex Virus). The…

Any future attempts to reduce the spread of Covid-19 should be focused on tackling close airborne transmission of the virus which is considered to be the primary route for its circulation, according to experts. Respiratory experts argue that it is now clear that SARS-CoV-2 is most likely to transmit between people at close range through inhalation rather than through contact with surfaces or…