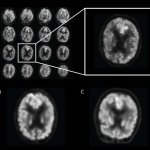
News • Artificial intelligence
AI predicts Alzheimer’s years before diagnosis
Using artificial intelligence, metabolic brain changes can be identified earlier leading to timely diagnosis and intervention of Alzheimer’s disease.

Using artificial intelligence, metabolic brain changes can be identified earlier leading to timely diagnosis and intervention of Alzheimer’s disease.

Built as the first commercially available scanner to deliver truly digital PET, the Vereos PET/CT, from Philips, offers revolutionary Digital Photon Counting technology. The science behind this scanner evolution is ‘quite complicated’, agrees Piotr Maniawski, Director of Clinical Science Nuclear Medicine at Philips Healthcare, yet the improved performance is significant, particularly when…
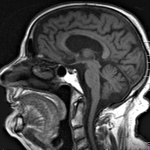
One day, MRI brain scans may help predict whether older people will develop dementia, new research suggests. In a small study, MRI brain scans predicted with 89 percent accuracy who would go on to develop dementia within three years, according to research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the University of California San Francisco. The findings, presented at the…
A world where machines can be controlled by thought alone – such is the promise of so-called brain-computer interfaces (BCI). BCIs are both hardware and software communication systems that read brain and nerve signals, convert those into electrical signals and translate human thoughts into machine commands. Developers of BCIs rely on artificial intelligence, neural network models and big data…

Virtual Reality (VR) technology is aiding trainee surgeons to practise complex procedures in a simulated setting, rather than learning skills on real patients. VR is also helping to demystify neurosurgery in that it enables medical students and patients to ‘enter’ and experience a neurosurgical operating theatre. Alex Alamri, a trainee neurosurgeon at Barts Health NHS Trust in London, UK,…

Imec, the world-leading research and innovation hub in nanoelectronics and digital technologies, released and is making available its state-of-the-art high-density neural probe, Neuropixels, to the global neuroscience research community. With almost a thousand electrodes, and 384 recording channels on a single shank, the Neuropixels probe provides an unprecedented resolution for mapping brain…

Chronic stress is a well-known risk factor for the development of psychiatric illnesses including depression disorders. The brain requires a great deal of glucose, and stress is known to alter glucose metabolism. However, if stress-associated mental impairments are linked to affected glucose metabolism remains to be seen. Researchers at the Department for Psychiatry and Psychotherapy at the Mainz…
The first successful surgery under anaesthesia occurred in the 1840s. Since then, people have been developing theories about what might be going on in the brain while a person is unconscious. Even after thousands of surgeries, researchers still don’t understand exactly which specific areas of the brain are responsible for transitioning into unconsciousness and back.

One in two women and one in three men will likely be diagnosed with dementia, Parkinson's disease, or stroke in their lifetime, estimate Dutch researchers in an observational study

Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports as many as five million Americans had the disease in 2013. They estimate that by 2050, nearly 14 million will have it. Age is the best known risk factor and memory loss is at the forefront of symptoms. Researchers of the Michigan Technological University investigate how technology can…
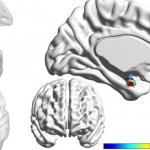
New research from the Westmead Institute for Medical Research and the University of Sydney has found that neurons deep inside the brain could hold the key to accurately diagnosing bipolar disorder and depression.
In healthy individuals, the Zika virus causes flu-like symptoms. If a pregnant woman becomes infected, the unborn child can suffer from severe brain abnormalities as a result of mechanisms that have not yet been explained. A study by the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry (MPI-B) shows that Zika virus proteins bind to cellular proteins that are…

A drug which has been used to treat liver disease for decades could help to restore cells damaged by Alzheimer's, a new study from the University of Sheffield has found. The pioneering study discovered the drug ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) improves mitochondrial dysfunction – which is known to be a causative factor for both sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease.
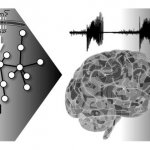
An international collaboration between Imperial College London, Singapore's Duke-NUS Medical School and Belgium-based pharmaceutical company UCB led to the discovery of a new anti-epileptic drug target and a whole new approach that promises to speed up the discovery of future drugs to treat debilitating diseases, such as epilepsy.
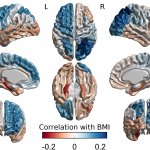
Clinicians should consider how the way we think can make us vulnerable to obesity, and how obesity is genetically intertwined with brain structure and mental performance, according to new research. The study, led by researchers at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital (The Neuro), was an examination of MRI and cognitive test data from 1,200 individuals, supplied as part of the Human…
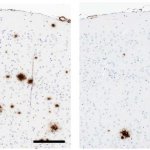
Researchers at the University of Florida have discovered that a modified version of an important immune cell protein could be used to treat Alzheimer's disease. The study reveals that soluble versions of a protein called TLR5 can reduce the buildup of amyloid plaques in the brains of Alzheimer's disease model mice and prevent the toxic peptide that forms these plaques from killing neurons.
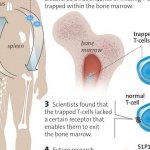
Glioblastoma brain tumors can have an unusual effect on the body's immune system, often causing a dramatic drop in the number of circulating T-cells that help drive the body's defenses. Where the T-cells go has been unclear, even as immunotherapies are increasingly employed to stimulate the body's natural ability to fight invasive tumors. Now researchers have tracked the missing T-cells in…
Neurologist who coined the phrase "Time is Brain" says message is not so simple anymore. Rather there should be no hard-and-fast rule governing when therapy can be given because strokes progress differently in different patients.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease is the most common hereditary neuropathy and affects more than two million people worldwide. In Germany, at least 30.000 people suffer from CMT which belongs to the class of rare disease. In a close collaboration, researchers at the Max-Planck-Institute for Experimental Medicine and the University Medical Center of Göttingen now hope to use lecithin, a harmless…

People who abstain from alcohol or consume more than 14 units a week during middle age (midlife) are at increased risk of developing dementia, finds a study in The BMJ today. However, the underlying mechanisms are likely to be different in the two groups. As people live longer, the number living with dementia is expected to triple by 2050. So understanding the impact of alcohol consumption on…

About a third of epilepsy sufferers require treatment through surgery. To check for severe epilepsy, clinicians use a surgical procedure called electrocorticography (ECoG). An ECoG maps a section of brain tissue to help clinicians identify areas damaged by seizures.

The electromagnetic radiation emitted from smartphones and similar devices may have negative effects on the memory of young people. Research conducted in Switzerland suggests that it might be a good idea to get rid of your smartphone from time to time.
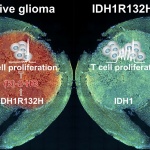
The exchange of a single amino acid building block in a metabolic enzyme can lead to cancer. In addition, it can impair the immune system. It thus blocks the body’s immune response in the battle against the mutant molecule and also impedes immunotherapy against brain cancer. This finding opens new insights into cancer development and progression and it also suggests that rethinking antitumor…

SLAC and Stanford researchers are developing a device that combines electrical brain stimulation with EEG recording, opening potential new paths for treating neurological disorders. It could help bring back lost brain function by measuring how the brain responds to therapies that stimulate it with electric current.
When light streams through her window in just the right way, Milena Canning will sometimes stoop to pick up a shiny coin she has noticed on the wooden floor of her Glasgow-area home. But her hand comes up empty – the 'coin' is just a dancing sunbeam, a quirk of perception in Canning's extraordinary world.