1920s drug shifts into today’s alcohol addiction arena
EH Paris correspondent Annick Chapoy, reports on a French study that confirms the relevance of a drug with a long history in the management of other diseases
EH Paris correspondent Annick Chapoy, reports on a French study that confirms the relevance of a drug with a long history in the management of other diseases

EyeMusic, developed by a team of researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, employs pleasant musical tones and scales to help the visually impaired "see" using music.
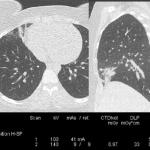
Imaging of the chest is the most common radiological examination worldwide. With the incidence of respiratory problems and lung cancer growing, all radiologists should be familiar with the appropriate imaging protocols. In a field dominated by chest x-ray (CXR) and CT, controlling radiation dose is mandatory.

Findings from the landmark National Lung screening Trial (NLST) continue to make waves in the United States, and increasingly around the world. The principal investigator for the component of the NLST sponsored by the American College of Radiology Imaging Network (ACRIN), Denise Aberle, MD, said the NLST can provide a road map for public policy regarding lung cancer screening, though she cautions…

Despite the increasing capabilities of CT to detect or identify disease, fungal infections continue to elude diagnosis by imaging. Paradoxically, a CT examination has been demonstrated to be a powerful tool, helping to identify a probability of infection among immuno-compromised patients early enough to effectively treat the condition.

“With all that has been published in the past year on this subject, we will not lack interesting things to highlight and discuss during this session,” said Martine Remy-Jardin, MD, Head of Cardio-Thoracic Imaging at the University Centre of Lille, who will present an update on CT Imaging for thromboembolic disease on Friday afternoon at ESTI 2012.

Will MRI become routine modality? Today, thoracic MRI is rarely performed in Europe. But this will change over the next decade, predicts Professor Hans-Ulrich Kauczor, Medical Director of the Radiology Clinic at University Hospital Heidelberg. He expects Germany to be at the forefront of this development because MRI technology, despite the high costs, is already widely used here and because CT…

The Johns Hopkins University (JHU), America’s first research university, in Baltimore, Md., USA, and the Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute (HHI), a mobile and information technology development leader based in Berlin, Germany, have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to jointly research the innovative medical applications of integrated optical sensors: small, highly sensitive devices with…

Volume-targeted ventilated premature babies have a higher survival rate and suffer less ventilation-related lung damage – this is the result of a survey amongst international neonatologists.

A new report from Siemens Financial Services (SFS) shows that annual growth rates for global medical equipment leasing and renting have now outstripped growth in the medical device market as a whole. The global medical leasing market is currently expanding at a rate of 6.50%, outpacing the 4.98% growth rate of the global medical device market.

Johns Hopkins experts in the prevention and treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis are calling for increased screening and more rapid testing of the 9 million people worldwide estimated to be infected each year with TB, and now at risk for this form of the highly contagious lung disease.

Making prostate cancer therapy more effective, more comfortable for patients and less expensive for society? Dose escalation, up to 80 Gy and above, may be necessary to successfully treat localised prostate cancer with radiotherapy (RT).

The European operating room solutions market, comprising surgical lights, surgical tables and pendants, is primarily a replacement market. Although tightening budgets are hindering market prospects, the need for state-of-the-art operating rooms are creating lucrative growth opportunities.
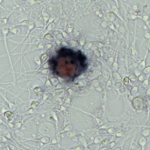
A team of researchers at Rigshospitalet has found a new and simple way of detecting testicular cancer before it starts. This discovery will benefit patients in both Denmark and abroad.

Anja Behringer reports on a neglected risk factor. With an aging population multimorbidity is increasingly a major challenge for hospital care. Diabetes is one of the medical conditions frequently encountered in multimorbid patients since cardiac and vascular diseases are often accompanied by dysfunctions of the blood sugar metabolism.

Meeting with EH editor Brigitte Dinkloh, Congress Secretary Professor Alexis Ulrich MD (left), Assistant Medical Director at the Clinic for General, Visceral and Transplant Surgery at the University of Heidelberg, outlined the scientific programme, discussed some impressive advances in surgical procedures, and explained why the gathering bears the slogan Surgery in Partnership.

Figures suggest that imaging of pregnant women increased by 121% between 1997 and 2008, even though radiologists face several critical challenges when imaging these patients.

If the hopes of inventors are to be believed, in around 20 years’ time there will be ‘real artificial lungs -- for now the endpoint of a history that began 84 years ago with the invention of the iron lung. Until then, non-invasive and invasive mechanical respiration will continue to dominate the hospital, complemented by extracorporeal procedures for blood oxygenation and decarbonisation,…

The world’s first gene cancer therapy study of an innovative oral vaccine is underway at the Surgical Clinic of Heidelberg University Hospital.

Obesity is physically debilitating – and costly for healthcare. Losing excess weight has positive effects on the entire metabolism and improves life expectancy. However, for patients who cannot lose their morbid, excess weight through diet, today’s surgical interventions can help towards permanent weight loss – and reduction in insulin dependency for diabetics.
Around for almost 20 years, minimally invasive technologies such as laparoscopy and robot-assisted surgery are popular subjects – and aired again during the 27th EAU Congress held in February at the Palais des Congrès, Paris.

A Birmingham hospital is pioneering a new procedure which aims to maintain and improve the quality of organs for transplantation in recipients on the waiting list.

Seriously injured trauma patients transported to hospitals by helicopter are 16 percent more likely to survive than similarly injured patients brought in by ground ambulance, new Johns Hopkins research shows.

Carefully adjusting mechanical ventilator settings in the intensive care unit to pump smaller breaths into very sick lungs can reduce the chances of dying by as much as 8 percent, according to a study by critical care experts at Johns Hopkins. Study participants were evaluated for two years after their acute lung injury.

Although the drug metformin is considered the gold standard in the management of type 2 diabetes, a study by a group of French researchers published in this week's PLoS Medicine suggests that the long-term benefits of this drug compared with the risks are not clearly established - an important finding given that currently, thousands of people around the world are regularly taking metformin to…