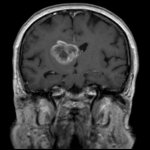
News • Glioblastoma
New actively personalized therapeutic vaccine for brain cancer
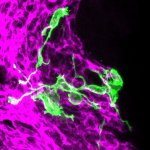
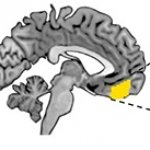
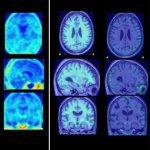
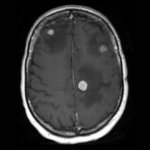
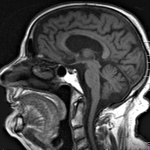
The prospect of an actively personalized approach to the treatment of glioblastoma has moved a step closer with the recent publication in Nature of favorable data from the phase 1 study GAPVAC-101, testing a novel therapeutic concept tailored to specific characteristics of patients’ individual tumors and immune systems. For the first time, the feasibility of such a highly personalized form of…