News • Deep learning approach
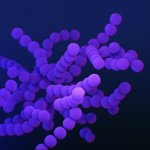
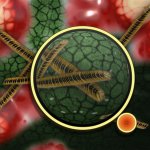
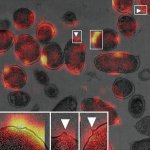
'Curvy' bacteria as telltale sign of drug resistance?
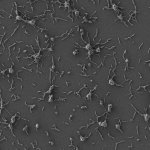
Researchers find that drug-resistant bacteria can be distinguished from non-resistant bacteria based on structural changes evident in electron microscope images with high accuracy using deep learning.