Molecular diagnostics
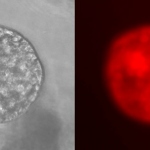
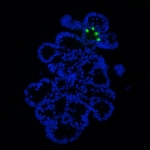
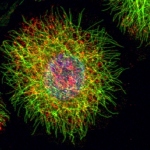
Research in the field is booming thanks to newly arriving methods to identify gene sequences. Scientists are interested in a wide range of issues from disease-relevant variations of human genetic information to the detection of viral genetic material that supports therapies. Several highlights of current research were presented this spring at the 9th International Symposium on Molecular…