News • Workload evaluation
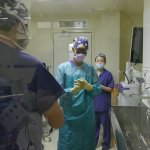
When anaethesiologists are spread too thin, more surgeries go wrong
A new US study indicates that the number of overlapping procedures managed by an anaesthesiologist increases the risk of death or complications after surgery.