News • MRSA
Decolonization protocol can prevent dangerous infections
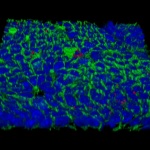
Antiseptic soap, mouthwash, and nose ointment after hospital discharge reduced infections and infection-associated hospitalizations due to MRSA in high-risk patients. Hospital patients who have methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) can prevent future MRSA infections by following a standard bathing protocol after discharge. The Changing Lives by Eradicating Antibiotic Resistance, or…