New MRI breast scanner from Siemens
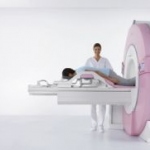
Siemens Healthcare recently presented its first MRI breast scanner, Magnetom Espree-Pink. The 1.5-Tesla system is the latest innovation in magnetic resonance imaging, featuring a dedicated solution for breast examinations. Particularly for obese and claustrophobic patients, the large, 70-centimeter magnet bore makes examinations more comfortable, or, in some cases, it makes them possible for the…