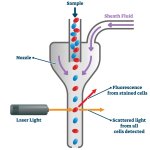
Article • Flow cytometry
Detecting and measuring nanoplastics in the blood stream
Plastics are a part of everyday life, and an increasingly concerning factor of global environmental pollution. They also have infiltrated our bodies as microparticles (MPs) and nanoparticles (NPs), found even in placentas supporting foetal life. And they are in our blood. Now, researchers in Spain have developed a new method to detect and measure nanoparticles in human peripheral blood that is…