News • Strategic cooperation
SpeeDx and Cepheid announce partnership on European distribution
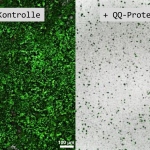
SpeeDx Pty, Ltd. announced an agreement with Cepheid for distribution of its PlexPCRTM and ResistancePlusTM molecular diagnostic products in key markets throughout Europe. The agreement, covering Germany, France, Italy, and the UK, will increase coverage for the market-leading ResistancePlus MG test, the first CE-IVD test for Mycoplasma genitalium to combine detection with testing for…