News • Imaging signatures
CT-based radiomics deep learning to predict lymph node metastasis in tumors
Researchers at University of Tsukuba have developed an imaging model to predict preoperative lymph node metastasis in nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors by combining radiomics (data analysis based on radiological images) and deep learning;
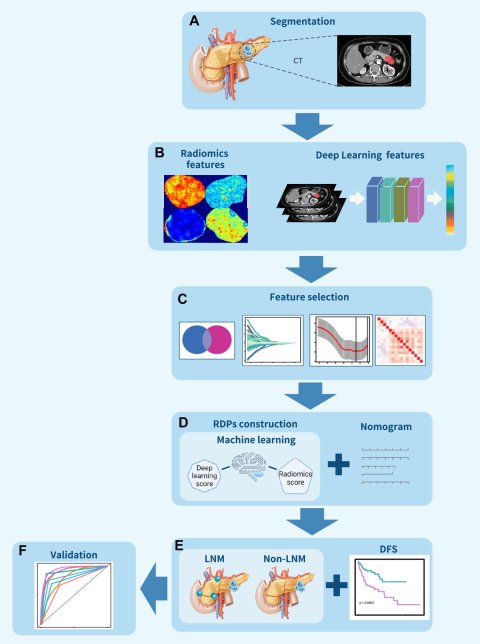
Image source: Gu et al., eClinicalMedicine 2023 (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
This model has been developed as a new method for noninvasively determining preoperative lymph node metastasis. This new model enables more accurate diagnosis and selection of treatment strategies.
Nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, while rare, are primarily treated through surgery. The presence or absence of lymph node metastasis considerably influences the selection of surgical and other treatment approaches. Particularly controversial is the necessity of surgery for tumors smaller than 2 cm as current clinical guidelines provide no clear consensus. Existing methods for preoperative diagnosis of lymph node metastasis are inadequate. To address the aforementioned challenge, the Tsukuba team has created a predictive model by integrating radiomics features extracted from CT and MRI images using artificial intelligence deep-learning techniques. The findings are published in the journal eClinicalMedicine.
The model has demonstrated an 89% success rate in predicting lymph node metastasis, a rate that rises to 91% when the model is validated with data from an external hospital. Furthermore, the performance of the model remains consistent, irrespective of the tumor size being larger or smaller than 2 cm.
Recommended article

Article • Radiology + data + AI = ?
Today and future radiomics
Radiomics is one of the most exciting topics in radiology. It involves data and artificial intelligence (AI) but very few people know or understand the details. In her lecture ‘How does Radiomics work?’, presented at the German Radiology Congress in Leipzig, Professor Ulrike Attenberger outlined how radiomics will advance radiology but also the obstacles faced along the way.
In conclusion, the model can help predict lymph node metastasis. Moreover, the model equips surgeons with a crucial tool for selecting the most appropriate surgical procedures and treatment strategies, potentially transforming patient outcomes in the challenging medical field.
Source: University of Tsukuba
23.01.2024