Efficient screening programmes
Engineer Dr W Schneider, of image diagnost GmbH discusses digital screening networks and multi-centre co-operation, based on automated DICOM communication. Along with its mammography solutions, image diagnost also specialises in developing concepts for regional and national digital screening networks
Modern methods and technology make it possible to combine out- and inpatient treatment through comprehensive, overlapping systems and to standardise and optimise early diagnosis, therapy and aftercare for malignant diseases of the female breast regionally.
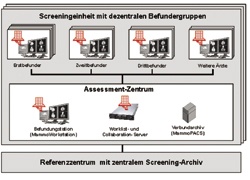
The introduction of standardised documentation and the opportunity to implement quality assurance programmes require the set up of suitable networks to complement the development of digital networks. They are of particular importance in mammography screening where multiple diagnoses are required and where a network significantly eases the workflow. The harmonisation and acceleration of processes, avoidance of information loss and the resulting effects, as well as the stimulation of a close co-operation between everyone involved, open up the opportunity to implement patient-oriented and, in the medium tern, cost-effective medicine.
Mammography screening networks can only be successful if suitable measures for quality assurance are introduced. The enormous volume of data generated through a quality assured diagnosis process can only be supported effectively through integrated technical concepts. Solutions based on the sending of images and results by post are no longer acceptable for mammography screening programmes; in fact they are counterproductive from an economic and quality assurance point of view.
Organisational structures, and networking concepts matched to them, should take into consideration geographical factors as well available expertise and technical equipment. Image diagnost GmbH of Munich therefore developed a concept for multiple diagnosis that is adaptable to these different concepts and is suitable for a central facility, as well as the development of networks linking outpatient and inpatient units.
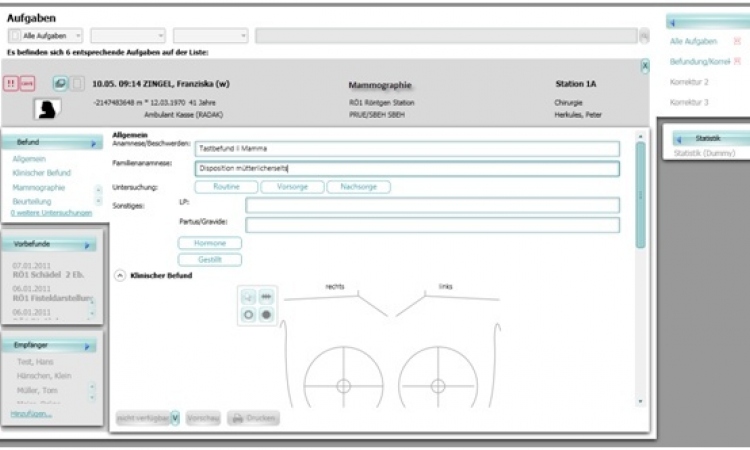
Graphically, a digital network with complete and standardised data recognition, which consists of a digital screening centre with several participating diagnosis groups, is sketched in an exemplary manner. The system can facilitate first, second and third diagnoses, assessment and central screening data collation and archiving, using the Worklist - and Collaboration Server developed by image diagnost. All digital diagnosis consoles, used instead of alternators, are equipped with a user-interface that can be used to monitor all data input and automated processes.
The Worklist- and Collaboration Server has been especially developed for screening networks. It generates different types of work lists based on adaptable rules and makes these accessible to all partner groups and partners within the network. This makes it possible to set up multi-locational workflow scenarios that allow for a patient and the person carrying out the diagnosis to remain anonymous.
Image- and diagnosis data are centrally stored for a screening network and are additionally backed up in a superordinate centre. Access permissions are monitored by the Collaboration Server and also can be manually manipulated via the diagnosis workstation. This makes it possible to make images and results temporarily accessible to other colleagues. The Collaboration Server guarantees consistent access to all data. A particular advantage for screening scenarios is that copies of data sets do not need to be stored in an archive file when mammography images are made accessible to other locations, thus saving on storage resources and avoiding unnecessary conflict situations.
The Dutch Breast Cancer Screening Programme BBNN is already using a version of the Collaboration Server developed by image diagnost in its mobile screening units (Mammo-Buses).
Other products from Image Diagnost include the MammoWorkstation, with possibilities for integration into existing infrastructures supplied by various manufacturers; the CAD-Server (Computer Aided Detection) for automated marking of potential malignant structures in a mammography image, and the Digitising Workstation for the secondary digitisation of film mammographies, based on EUREF guidelines.
The system is an inexpensive first step into the world of digital mammography and the DICOM-shuttle as the key element for automated image and results transmission with high quality image compression.
01.07.2004