Breathalyzer
Clinical Laboratories Could Soon Diagnose 17 Diseases with Single Breath Analyzer Test
The Technion breathalyzer would give pathology groups and medical laboratories unprecedented ability to support physicians in diagnosing and treating cancers, chronic diseases, and other illnesses.
Assuming the cost per test was at a competitive level to existing technologies, what would give this new diagnostic system appeal to physicians and patients alike is that it would be a non-invasive way to diagnose disease. Only a sample of the patient’s breath would be needed to perform the assays.
Researchers at the Israel Institute of Technology, or Technion, published the results of their study in ACS Nano, a monthly journal of the American Chemical Society devoted to “nanoscience and nanotechnology research at the interfaces of chemistry, biology, materials science, physics, and engineering.”
AI Discerns Chemical ‘Fingerprints’ of Disease
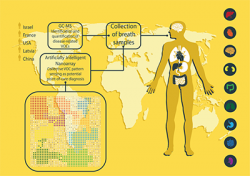
The breathalyzer works by examining volatile organic compounds (VOCs) contained in exhaled breath to discern a medical condition. VOCs are a group of organic, carbon-based chemicals that evaporate quickly and easily at room temperature.
After the study participants exhaled into the machine, the researchers used artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze the number of VOCs in each breath and examine the VOC concentration patterns to determine if an illness was present. The researchers then examined the chemical structure of the breath samples and found 13 chemical components, in different compositions, in all 17 of the diseases.
Hossam Haick, PhD, of the Chemical Engineering Department at Technion was the lead author and researcher of the study.
“Each of these diseases is characterized by a unique fingerprint, meaning a different composition of these 13 chemical components. Just as each of us has a unique fingerprint that distinguishes us from others, each disease has a chemical signature that distinguishes it from other diseases and from a normal state of health,” stated Haick in a Technion article on the new breathalyzer test. “These odor signatures are what enables us to identify the diseases using the technology that we developed.”
The 17 different illnesses and unrelated diseases that can be detected by the device are:
- Bladder cancer;
- Colorectal cancer,
- Chronic kidney disease;
- Crohn’s disease;
- Head and neck cancer;
- Irritable bowel syndrome;
- Kidney cancer;
- Lung cancer,
- Multiple sclerosis,
- Ovarian cancer;
- Parkinson’s disease;
- Pre-eclampsia;
- Prostate cancer;
- Pulmonary hypertension;
- Stomach cancer; and
- Ulcerative colitis.
Breath samples for the vital research were collected at nine medical centers in five different countries: China, France, Israel, Latvia, and the US. The breath test was administered to 813 patients who had previously been diagnosed with one of the 17 diseases, and to 591 control subjects from the same locations. Researchers found the breathalyzer could successfully identify individual diseases with an 86% accuracy rate.
Clinical laboratory ‘Breath-print’ Tests Diagnose and Monitor Disease
Exhaled breaths, or “breath prints,” consist of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, oxygen, and minute amounts of other chemicals. The individual’s state of health determines the amount of each element to be found in the breath. Thus, each new breath print becomes an indicator of the patient’s condition at that time making it highly useful for both diagnosing and monitoring chronic disease, infections, and common illnesses.
Breath prints may prove to be vital tools in the clinical laboratorian’s arsenal. The utilization of VOC biomarkers in exhaled breath to identify diseases is advantageous because the non-invasive test is well tolerated by patients and very easy to use.
“Breath is an excellent raw material for diagnosis” said Haick in the Technion article. “It is available without the need for invasive and unpleasant procedures, it’s not dangerous, and you can sample it again and again if necessary.”
Further testing is needed before the device will be ready for the market, but Haick and his team are hopeful it will be an affordable and easy-to-use tool for disease diagnosis.
“This is a new and promising direction for diagnosis and classification of diseases, which is characterized not only by considerable accuracy, but also by low cost, low electricity consumption, miniaturization, comfort, and the possibility of repeating the test easily,” concluded Haick in the Technion article.
Over the past 20 years, there has been much research into ways to use a breath specimen to diagnose disease. Among the most intriguing have been clinical studies that demonstrated how specially-trained dogs could discern patients with certain cancers from patients who were healthy. It was in the 1990s when a clinical laboratory test for H. pylori was introduced that used a breath sample to identify if the bacteria were present or not. Many clinical laboratory scientists are familiar with this early use of a breath specimens to diagnose a specific bacterial infection.
Source: JP Schlingman, Dark Daily
27.03.2017