News • Finding treatment for Parkinson's disease
Synthetic neurons could take brain research to the next level
The body can recover from many things, but the damage caused by Parkinson’s disease isn’t one of them.
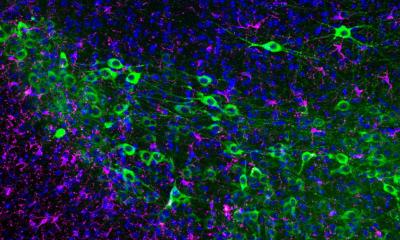
Image source: Purdue University photo/Chongli Yuan
No cure exists for Parkinson’s, which 1 million people in the U.S. are expected to be living with by 2020. But an outright cure isn’t the primary objective of research by Chongli Yuan, a Purdue University chemical engineering professor and leader of Purdue’s section of a multidisciplinary team studying the possibility of building synthetic neuron cells. “If we can replace part of those neurons, then we can have infinite possibilities in disease treatment in the future,” Yuan said. Parkinson’s disease occurs when neurons either die or are damaged, restricting their production of the brain chemical dopamine. Less dopamine results in the movement problems associated with the disease.

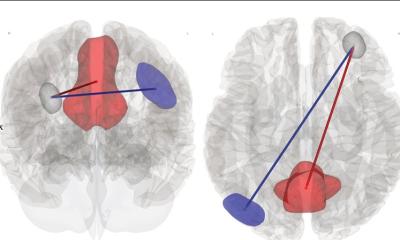
Image source: Purdue University photo/Vincent Walter
“When the neuron dies or becomes impaired like that, the brain has to get rid of the damaged neurons, and once they’re gone, they’re just gone,” Yuan said. “That’s why there’s no effective treatment for neurotrauma diseases. But creating a synthetic neuron could essentially be the solution for anything that requires the replacement of neurons in the brain or the nervous system.”
Yuan and her group received part of a $4 million award from the National Science Foundation’s 10 Big Ideas Challenge. The research is part of a four-year project shared among university researchers at Michigan, Stanford, Johns Hopkins, Rochester Institute of Technology, Baylor and the University of California, Santa Barbara.
The team’s plans are to divide neurons into essential building blocks and construct each building block through the incorporation of inanimate materials, such as proteins and lipids. The building blocks are then assembled into functional subunits capable of performing part of neuron or neuronal network functions. “This project is about using a bottom up approach to make a synthetic neuron,” Yuan said. “We will take all the information that biologists and neuroscientists have generated in terms of understanding how the brain works and how the neuron works, and we’ll use an engineering approach to construct it.”
Once a minimal neuron has been constructed that has all the essential functions, the project will focus on neurons’ job of processing information by recreating their ability to communicate between cells.
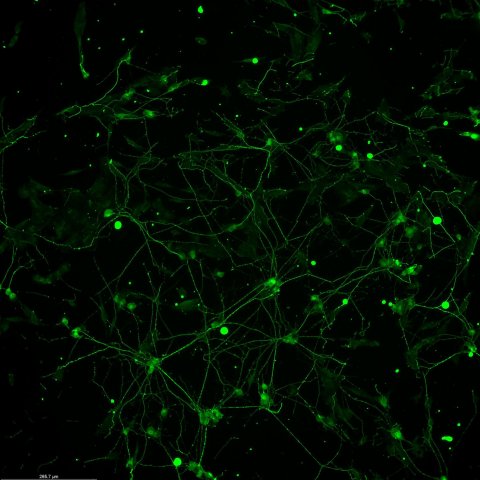
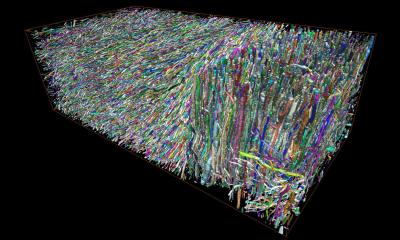
Image source: Purdue University photo/Chongli Yuan
Yuan said the team will work to have neighboring synthetic neuron cells communicate in positive and negative signals. If that’s achieved, the goal is to have a working binary response that is essential for information processing.
The research team is dedicated to breaking new ground in building synthetic cells by having a working basic neuron unit that will offer a platform to keep adding components to in order to eventually understand how the brain works. “We think the work is going to be challenging because whenever you try to mimic something that nature has made, nature has millions of years to do its very best job. We only have four years,” she said.
Source: Purdue University
13.01.2020