Spinal cord repair: pilot trials within sight
Injury to the brain and spinal cord cause permanent damage because, unlike bone and skin tissues, they lose the ability to repair themselves soon after birth.
Some experts suggest this is due to an inability to form new connections, others think the adult nervous system produces molecules that stop the growth of nerve fibres.
Both theories are disputed by Dr Geoffrey Raisman, at the National Institute of Medical Research, who points out that the brain constantly changes as we learn throughout life, and that cut nerves ‘sprout vigorously’, albeit not in the right direction. He suggests that adult nerve fibres fail to regenerate because they have to contend with much greater distances and much more complex pathways than those in the embryo.
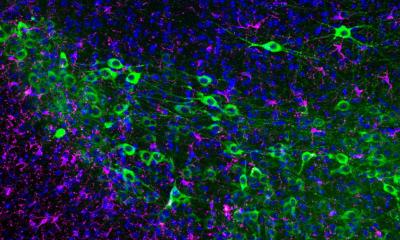
Scarring is another problem with healing spinal cord injuries. During development, nerves grow along glial cells (types of supporting tissue arranged in regular networks and channels). When glial cells are damaged each type behaves differently - some swell up, others die and some move into the damaged area, which is swamped with blood cells. The resulting scar blocks nerve fibres.
Dr Raisman has now developed a new and novel method for spinal cord regeneration, and this could soon lead to a human pilot study.
Using rats with injured spinal cords, Dr Raisman and team navigated around scar tissue by grafting a culture of glial cells from olfactory nerves (which regularly regenerate even in adults), onto the scarred section. These then grew into a ‘bridge’, through which the severed nerve fibres could follow, growing safely inside the sheath of graft cells and finding their way to the right targets in the rat’s brain.
The shift to humans
Dr Raisman’s team successfully restored nerve functions in rats with Partially severed spinal cords, and they believe their method ‘really is predictive of human repair’. They report that more work needs to be done on sourcing enough suitable graft cells and refining the implantation technique, and suitable patients must be found for a pilot trial. However, he hopes to overcome these final obstacles in the near future. Currently, discussions are underway, with the Institute of Neurology at University College London, about a possible trial at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery.
Details: Royal Society of Medicine Journal, June. www.rsm.ac.uk
01.07.2003