Source: Bavarian Broadcasting
News • Aerosol study
Singing in times of COVID-19: more space to the front than to the side
How high is the risk that aerosol transmission during choral singing could cause infection with the coronavirus? After occurrences of infection among choirs in the USA and Germany, Bavarian Broadcasting carried out a complex series of experiments for its musical ensembles in conjunction with the LMU University Hospital Munich and the Universitätsklinikum Erlangen (FAU). Initial partial results of the as yet unpublished scientific study are now available. In the study, the scientists involved explain the conditions they consider necessary – with regard to distance between the singers and the properties of the room’s indoor climate – for singing to remain a healthy activity during COVID-19.
Susanne Vongries, manager of the BR Chorus, describes the initial situation: ‘After the initial shock of lockdown and once we’d reviewed the restrictive guidelines, we quickly started to think about how we could resume working as musicians and what repertoire we could perform, with the condition that protecting our choir members and their health was our top priority.’
However, since there is very little reliable scientific knowledge available worldwide, particularly regarding the risk of infection for choral ensembles, Bavarian Broadcasting sought expert advice from Prof. Matthias Echternach, head of the Division of Phoniatrics and Paediatric Audiology at the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, LMU University Hospital Munich and himself a trained singer.
Recommended article

News • Aerosol propagation study
Covid-19: is it safe to play the trumpet and other wind instruments?
Aerosol generated by playing woodwind and brass instruments is less than that produced when vocalising (speaking and singing) and is no different than a person breathing, new research has found. The findings could be crucial to developing a roadmap for lifting Covid-19 restrictions in the performing arts, which have been significantly restricted since the start of the pandemic.
The study concept
Prof. Echternach, together with Dr Stefan Kniesburges, a specialist in fluid mechanics at Universitätsklinikum Erlangen (FAU), designed a study to measure the emission and distribution of both larger droplets and the smallest particles – known as aerosols – during singing with and without words and during speaking. The particular focus here, in contrast to studies that examine the flow velocities of particles, was that these experiments investigated the transmission and distribution of droplets and aerosols within a room.
To achieve this, the scientists constructed two experimental sets in Studio 2 at Bavarian Broadcasting’s studio in Unterföhring, Munich. Between 20 and 26 May 2020, ten test subjects from the BR Chorus and nine wind players from the BR Symphony Orchestra took it in turns to sing, speak and play specific passages at different volumes on these two sets. Data from the wind instrument measurements are still being evaluated.
Recommended article

News • COVID incidence at airports and in hospitals
Biosensor to detect coronavirus in crowded places
A team of researchers from Empa, ETH Zurich and Zurich University Hospital has succeeded in developing a novel sensor for detecting the new coronavirus. In future it could be used to measure the concentration of the virus in the environment - for example in places where there are many people or in hospital ventilation systems. Jing Wang and his team at Empa and ETH Zurich usually work on…
Measuring visible aerosol clouds
The first set used high-speed cameras and laser equipment to allow the scattering of larger droplets to be investigated. How are these droplets emitted from the mouth or the instrument, and which spoken or sung passages produced the largest quantity of droplets?
On the second set, cameras and white light were used to analyse how the even smaller aerosols leave the mouth and nose and how these spread within the room. In order to render the distribution of these tiny particles visible, the test subjects inhaled a carrier solution from e-cigarettes. This was then visible in bright light during and after vocalising.
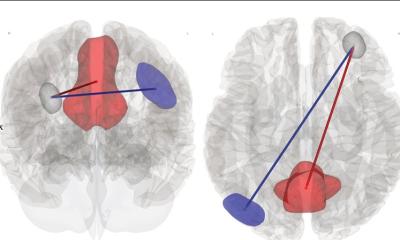
Evaluating the measurements of the aerosol clouds emitted showed that choir members would need to maintain a greater distance from colleagues in front of them than from those at either side. However, this presupposes that the aerosol is regularly removed from the room via a constant flow of fresh air. Even better would be to have partitions between the singers.
‘For the sung text, we measured distances from the centre of about one metre forwards, but some singers also achieved widths of 1 to 1.5 metres. That means that safe distances of 1.5 metres are probably too low and distances of 2 to 2.5 metres seem more sensible’, says Prof. Echternach. ‘However, the data only refer to direct transmission at natural speed during singing. For the singers’ safety, it’s important that the aerosols are also continuously removed from the room so that there’s no accumulation,’ he adds. ‘We noted significantly smaller distances towards the side than towards the front, meaning that distances here could be lower’, says Stefan Kniesburges. ‘But a constant supply of fresh air is required here as well, so as to remove aerosols from the air.’
Singing in a mask?
According to Kniesburges, tests with face masks revealed that ‘singing with surgical masks filters out the large droplets completely and the aerosols partially, but a portion of the aerosols are emitted in a jet-like fashion slightly upwards and to the sides.’ This occurs because the masks do not seal totally at the sides and over the nose. The researchers found that singing with a mask could be an option, as it reduced particle leakage, but this is not really suitable for professional choirs: ‘You have to be able to articulate well and of course you need every little nuance of sound,’ says Echternach. He does, however, think that church or other non-professional choirs may sing with masks for the preventive effect.
Source: LMU University Hospital Munich
04.07.2020