Sea Squirt Pacemaker Gives New Insight Into Evolution Of The Human Heart
An international team of molecular scientists have discovered that star ascidians, also known as sea squirts, have pacemaker cells similar to that of the human heart. The research, published in the JEZ A: Ecological Genetics and Physiology, may offer a new insight into the early evolution of the heart as star ascidians are one of the closest related invertebrates to mammals

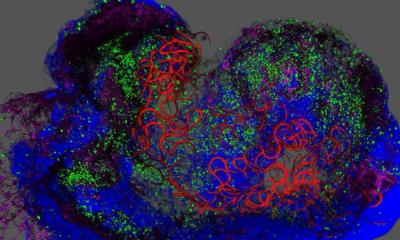
The research team, led by Annette Hellbach from the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Germany, expected to find clusters of HCN cells, the markers for pacemakers, at either end of the Botryllus schlosseri ascidian heart.
"The Botryllus schlosseri heart beats from one end to the other, stops for a short while and then starts to beat in the other direction," said Hellbach. "It would make sense to have two pacemakers on both ends from which the heartbeat is initiated, however, we found several HCN positive cells spread along the cardiac tube."
The team interpreted this finding as an evolutionary precursor to the elaborate cardiac conduction system found in mammals which are made up of clusters of pacemaker cells located in defined spots.
The team found that in comparison the cells in the B. schlosseri heart appeared to be randomly distributed along the heart; however, as with mammals the HCN cells played a vital role in generating the heartbeat.
The team also found that the cells responded to the blocking chemicals Cilobradine and Zatebradine by decreasing the heartbeat as is found to be the case for mice. This increases the likelihood that the cells operate through a similar molecular function.
"Our study reveals that the presence of HCN channels and their role in generating the heartbeat is shared between B. schlosseri and mammals," said Hellbach. "This makes colonial ascidians such as B. schlosseri insightful models for studies on the origins and evolution of vertebrate innovations, such as the pacemaker."
Sources: Wiley-Blackwell, AlphaGalileo Foundation.
11.08.2011