Research
Resolving a lymphatic riddle
For over one hundred years, scientists have debated the question of the origins of the lymphatic system – a parallel system to the blood vessels that serves as a conduit for everything from immune cells to fat molecules to cancer cells. This issue has now been resolved by Dr. Karina Yaniv of Weizmann Institute’s Biological Regulation Department. In a study reported in Nature, she and her team revealed how the lymphatic system develops in the embryo and for the first time managed to grow lymphatic cells in the lab.
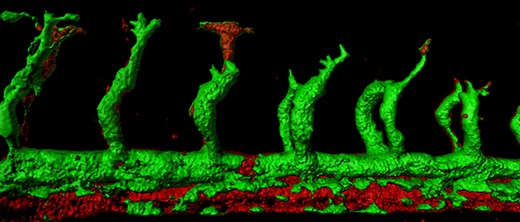
Some scientists had claimed that the lymphatic system was derived from specialized stem cells called angioblasts, whereas others had argued that it originated by the differentiation of pre-existing embryonic veins. It was the latter model that had ultimately become the accepted view. But as the research in Yaniv’s lab progressed, it became clear that scientists on both sides of the argument had been right: Lymphatic cells do indeed grow from veins, but they originate from a niche within the vein that harbors angioblasts.
In the initial stages of the research project, Yaniv’s team members Julian Nicenboim and Dr. Guy Malkinson obtained images of developing zebrafish embryos, whose transparent bodies make it possible to document embryonic development in real time over several days. The scientists then played the movies backward, to identify the point at which the lymphatic system began to form. To their surprise, they discovered that the cells that give rise to lymphatic vessels always originated in the same part of the embryo’s major vein. In that spot, the scientists found a niche of angioblasts, those same cells that a hundred years earlier were thought to be the source of lymph vessels, but were later neglected.
An in-depth genetic analysis, performed with the participation of graduate students Tal Lupo and Lihee Asaf, pointed to a gene called WNT5B, which was revealed to be the factor prompting stem cells to differentiate into lymphatic cells. When postdoctoral fellow Dr. Yogev Sela added WNT5B to human embryonic stem cells, these cells indeed differentiated into lymphatic cells – the first time such cells had been grown in the lab. “We started out by imaging zebrafish, and ended up finding a factor that makes it possible to create lymphatic cells,” says Yaniv. “That’s the beauty of research in developmental biology: The embryo holds the answers, and all we have to do is watch and learn.”
Aside from the feat of answering the longstanding question of how the lymph system arises, understanding how it forms and develops can provide important insights into disease, from metastasis to the abnormal accumulation of lymph fluids, particularly in the wake of surgery to remove cancerous tumors.
Source: Weizmann Institute of Science
16.07.2015