Research on small RNA molecules could bring new therapies
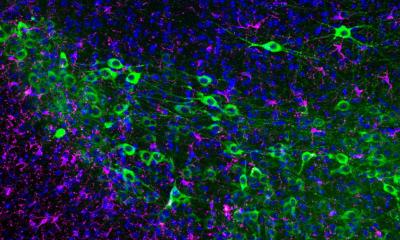
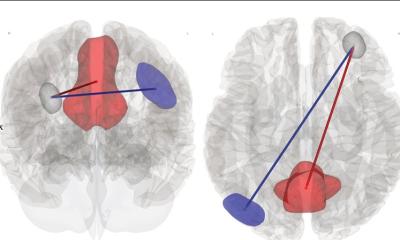
The discovery of small RNA molecules and their relevance for gene regulation has dramatically changed our understanding of many essential cellular processes - and provides the opportunity to develop new ways for treating various diseases.
By selectively inhibiting gene expression and thereby ‘silencing’ genes involved in pathogenesis, the RNA molecules constitute a unique tool to treat cancer, neurological disorders or viral infections and other human diseases. At the XX International Congress of Genetics, held in Berlin (12-17 July) experts will present results from the latest research in RNA biology and discuss potential applications.
‘Today, small RNAs are increasingly developing into a therapeutic tool and there is reasonable hope that this will be successful in the near future,’ explained Professor Alfred Nordheim, Secretary General of the XX International Congress of Genetics.
Apart from RNA genetics, modern genetic research is already contributing much to combat diseases. In recent years, improved sequencing techniques made possible the rapid diagnosis of infectious bacteria or other pathogens. Bacterial cultures of patient specimens, which often take days to grow in the lab, thus become redundant, and effective therapies can be implemented sooner. ‘There is hardly a
disease without a genetic component’, the professor observed. ‘Not only pathogens, but also food, lifestyle or radiation can make us sick by influencing and changing our genetic information, or its expression. We are now beginning to understand the functioning of a cell on the molecular level.’
30.04.2008