Image source: Adobe Stock/Axel Kock
News • Lifetime changes unraveled
Researchers track the process of breast cancer formation
From the early stages of cell mutations starting in puberty to their manifestations as breast cancer in later years, the entire process has remained shrouded in mystery.
Now, a team of researchers at Kyoto University has revealed the mechanism by which breast cancer is formed in the cells of mammalian epithelium, whose main function is to secrete milk. According to the team's first analysis, approximately 20 mutations accumulate annually in each epithelial cell until menopause. After menopause, however, the mutation rate significantly decreases. "Additionally, our results suggest that estrogen influences mutation accumulation in mammary epithelium, which correlates with our discovery of decreased accumulation after childbirth," says corresponding author Seishi Ogawa of KyotoU's Graduate School of Medicine.
The researchers published their findings in the journal Nature.
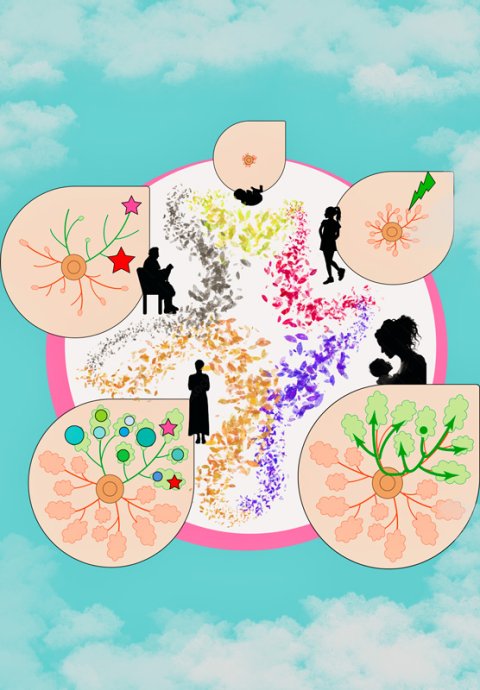
Image credit: KyotoU Global Comms/Tomomi Nishimura
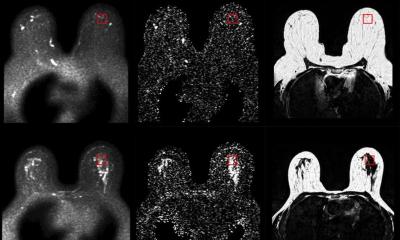
As 70% of breast cancers are understood to be estrogen-sensitive, Ogawa's team may shed light on estrogen's role in the initiation of breast cancer. Further investigation of the genetic relationship between breast cancer, its surrounding lesions, and normal epithelial cells led to mapping breast cancer's translocation-positive expansion. During this expansion process, cells of multiple origins that would subsequently develop breast cancer manifested themselves at the average age of 30.
Previous studies have focused on driver mutations -- the genetic changes in cells that are already cancerous -- leading to abnormal growth. But these findings only paint a partial picture of the process and do not reveal the timing and order of driver mutations or cancer formation. "Normal-looking tissues may already contain numerous populations of non-cancer cells -- or clones -- that have acquired mutations in cancer-related genes," says co-author Tomomi Nishimura of KyotoU's Graduate School of Medicine.
After examining the similarities and differences in the mutations of both cancer and non-cancer lesions originating from the clones, the team reconstructed an evolutionary tree to visualize the unique pattern of cancer evolution. "Our study brings us closer to exposing the clinical profile of estrogen-sensitive breast cancer, particularly in pre-menopausal women, potentially aiding cancer risk monitoring and prevention," adds Ogawa.
Source: Kyoto University
05.09.2023