Muscle health
CTs can detect more than just broken bones
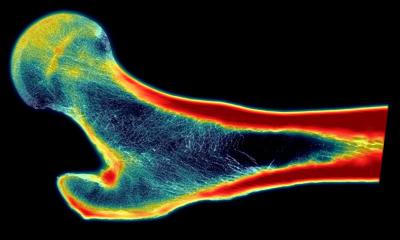
Using computed tomography (CT) to evaluate muscle health may help identify optimal treatments for older patients who fall and break their hips, a new study led by radiologists from UC Davis and Wake Forest Baptist medical centers has found.
The research specifically showed that decreased "core" muscle that stabilizes the spine was associated with decreased survival times following hip fractures. While CTs of core muscle have been used to predict patient outcomes, the new study is the first to use the imaging technology to link survival with hip fractures, a common cause of injury, hospitalizations and disability among older Americans.
Doctors could potentially use information about muscle loss, known as sarcopenia, to determine a patient's level of frailty and guide treatment decisions, according to lead author Robert Boutin. A patient with favorable life expectancy, for instance, could be treated for hip fracture with total hip arthroplasty, resulting in lower reoperation rates, better hip function and better quality of life. In contrast, a patient with clinical and imaging features of frailty could benefit most from a simpler surgery. "As patients age, it becomes increasingly important to identify the safest and most beneficial orthopaedic treatments, but there currently is no objective way to do this," said Boutin, a UC Davis professor of radiology. "Using CT scans to evaluate muscles in addition to hip bones can help predict longevity and personalize treatment to a patient's needs. We're excited because information on muscle is included on every routine CT scan of the chest, abdomen and pelvis, so the additional evaluations can be done without the costs of additional tests, equipment or software."
The study included nearly 300 people who were at least 65 years of age and treated for fall-related injuries at UC Davis Medical Center between 2005 and 2015. All were suspected of breaking their hips and received CTs to diagnose or rule out fracture. The researchers evaluated the CTs with additional measurements of the size and density of lumbar and thoracic muscle alongside the spine. That information was then compared with mortality data from the National Death Index, a centralized database of death record information maintained by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The results showed that patients with better core muscle had significantly better survival rates over the duration of the 10-year study.
The study is especially important because most prior research on CTs of muscle has been in cancer patients and involved larger sample sizes, according to senior author Leon Lenchik. "The fact that we were able to predict survival in such a small group of non-cancer patients is truly remarkable," said Lenchik, professor of radiology at Wake Forest. The authors hope their work will inspire additional studies of sarcopenia, which is epidemic worldwide, and research focused on improving orthopaedic treatments for older patients. "Recognizing sarcopenia as a distinct condition that provides clues to future health can open doors to new discoveries in diagnosis and treatment," Boutin said.
Source: UC Davis Health
07.06.2017