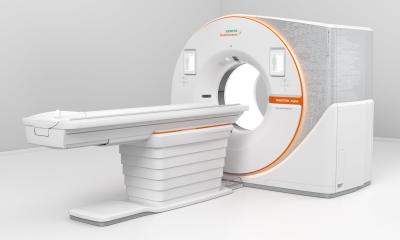
Breast Care Solutions from Siemens at the German Radiology Congress
Siemens Healthcare was presenting its latest solutions for the early detection and treatment of breast cancer at the German Radiology Congress in Berlin. These Breast Care Solutions include a variety of imaging procedures, such as ultrasound, mammography, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), supplemented by IT and laboratory diagnostic solutions. Siemens places special focus on the third dimension: three-dimensional imaging of the female breast using two of the latest Siemens technologies, the Automated Breast Volume Scanner (ABVS) with Acuson S2000 ultrasound system, and 3D tomosynthesis with the digital mammography system, Mammomat Inspiration.
They enable physicians to discern far more detail than previously. The first radiologists and hospitals in Europe and Asia are already
working with these new technologies. At a separate Siemens symposium on the subject of “Breast Care”, experts were reporting on the innovative diagnostic capabilities and their initial experiences. The objective is a more precise and faster diagnosis, as well as improved examination quality and therapy for the patient.
This multimodality approach – combining various imaging procedures such as ultrasound,
mammography, magnetic resonance imaging, as well as molecular imaging – for combating breast disease (senology) is gaining in popularity among physicians. The new technologies provide improved image quality and optimized workflows to support physicians in their work. As a result, more patients can be examined in less time. The innovations also help reduce the number of biopsies and improve the planning of necessary surgeries. Immunodiagnostic tests provide supplemental information regarding the course of therapy. The following presents the latest developments for “Breast Care" in detail:
Digital mammography system, Mammomat Inspiration
The digital full-field system, Mammomat Inspiration, has been on the market since the end of 2007. The system is successfully in use at more than 500 hospitals and physicians’ offices worldwide. Many new components provide the physician with improved imaging of the female breast, simplifying diagnosis. At the same time, the novel MoodLight function makes the examination more comfortable for women than conventional mammography units. A host of functions and technical details enable the radiation exposure to be tailored to the individual woman and thereby kept as low as possible. In addition, the physician can perform stereotactic biopsies easily and automatically at the Mammomat Inspiration using the optional biopsy unit.
During 3D breast tomosynthesis, a further development of digital mammography, the X-ray tube of the Mammomat Inspiration moves about the compressed breast. A total of 25 low-dose exposures with up to two images per second are acquired. The data are then converted into a 3D data record.
Using this technology, tumors can be displayed that were previously hidden in conventional
mammography due to overlapping tissue. This makes for more precise diagnoses and reduces the number of false-positive diagnostic reports. To date, numerous Mammomat systems have been installed with tomosynthesis in Europe and Asia.
Dr. Renate Tewaag of the Radprax-Group, a group practice for radiology, nuclear medicine, and radiation therapy in Wuppertal / Germany – has been working with 3D tomosynthesis for several months, the first radiologist in Germany to do so. "With tomosynthesis we are witnessing a fascinating further development in digital mammography. This 3D technology offers impressive improvements in the detection of detail, which benefit both patients and radiologists alike: We can be more certain in our diagnosis, while women being examined can feel more reassured," explained Dr. Tewaag. "Tomosynthesis makes mammography less stressful for both the physician and the patient. Based on current first impressions, additional examinations and interventions can be avoided with a clear conscience. Lesions hidden within the dense glandular tissue are identified at an earlier stage."
As a supplement to 3D tomosynthesis, Siemens offers Syngo MammoReport, the multi-modality workplace for breast care. For the first time, images from the 3D tomosynthesis, 3D ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging modalities can be displayed together at a workstation and used for compiling diagnostic reports.
Ultrasound for early breast cancer detection
The Siemens Acuson S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner (ABVS) supports the
physician particularly in diagnosing very dense breast tissue using a more precise, threedimensional acquisition technique. The first of these new ultrasound breast scanners has recently gone into use by radiologists and gynecologists at hospitals and physicians offices in Germany and Europe. Dr. Frank Stöblen of the Diavero Diagnostic Center in Essen / Germany is one of the first physicians to use the new ultrasound technology. “The ABVS
system is a fascinating enhancement of the previous, manually-guided ultrasound
examination method. The automation always produces the same image quality, regardless of
the examiner.”
With the Acuson S2000 ABVS, Siemens Healthcare is the first to introduce a multifunctional
ultrasound breast scanner that automatically acquires volume displays of the female breast.
The user-independent, standardized examination has thereby gained in significance. Dr.
Frank Stöblen, the radiologist and co-owner of the Diavero Diagnostic Center in Essen, is
certain that the new ultrasound system with ABVS will continue gaining in importance for
breast cancer diagnosis: “This technique will become important for early detection. It can also be used to examine high-risk patients, for example those with a genetic predisposition or
those undergoing or having completed cancer treatment." In addition, these 3D acquisitions
can also display the coronal plane of the breast (from the nipple to the breast wall) in slices,
which to date has not been possible in conventional ultrasound imaging. This coronal view
simplifies and accelerates diagnoses, and is a valuable instrument in surgical planning.
Another ultrasound examination method is called elastography. The technology named “eSie
Touch Elasticity Imaging” is based on the principle of showing elasticity, and displays the various strain properties of tissue. According to the American Cancer Society, 80 percent of all biopsied breast lesions are benign. The medical community hopes to use this method to reduce the number of unnecessary invasive breast biopsies. The new application enables the physician to characterize breast lesions with a much higher degree of precision. Tissue with a low compression profile is an indicator for malignant changes. Ultrasound in combination with mammography is the method of choice for women with dense breast tissue. In Europe and North America, this is the case for two in five women.
Innovations in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for breast cancer screening
Abnormalities in breast tissue can be clarified with an MRI examination. This method offers many advantages: for example, it does not subject patients to radiation. In addition MRI, in contrast with other modalities, displays the various breast tissue types as well as the tumor angiogenesis (newly formed blood vessels that supply the oxygen and nutrients the tumor requires to grow). MRI is particularly suited for young women with dense breast tissue, women with breast implants, women who have previously undergone multiple surgeries, and for detection of DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ).
With its Magnetom family of magnetic resonance imaging systems, Siemens offers a
comprehensive portfolio of 1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla scanners with a variety of special applications and coils for breast imaging. In addition, Siemens has developed a dedicated scanner for breast imaging: the Magnetom Espree Pink. Particularly for obese and claustrophobic patients, the large 70 cm magnet opening makes examinations more comfortable than with previous systems, and in some cases possible for the first time. Patients can be positioned head first or feet first as required.
For patients who felt cramped in earlier systems, the design of the Magnetom Espree Pink is very beneficial. Biopsies are also possible as an enhancement to this MRI breast scanner. Additional software applications enable three-dimensional post-processing of the breast and ensure clear images, even if the patient moves a little.
Special software packages for MR breast imaging were also developed to support physicians. These include the new Syngo BreVis diagnostic reporting software. It displays all examination results for a patient in a single view – for example ultrasound and radiography images in addition to magnetic resonance images – not possible with previous technology. The physician can also use the new Syngo BreVis Biopsy interventional software when necessary to plan and perform a biopsy. It is almost fully automated and much faster than before. As such, this simple and efficient application is a major advance for patients and users.
“Normally I need up to 20 minutes to be able to evaluate a breast image. With the new syngo
BreVis software, I only need about five minutes to review the case. The first time I tried it, it was so fast I had to ask whether I had configured my settings correctly. I felt so uncomfortable I evaluated all of the patient cases again using conventional methods in order to be certain. I got the same results and had not overlooked anything. Syngo BreVis is brilliant and significantly improves workflow. It helps me and my patients save time while providing the same diagnostic quality reporting,” said Dr. Marie-Anne Labaisse, radiologist at the Centre Hospitalier de Wallonie picarde, Tournoi, Belgium.
Molecular imaging in breast cancer diagnosis
At the German Radiology Congress, Siemens will present applications of various molecular
imaging procedures for the diagnosis and therapy of breast cancer. Many types of cancer –
including breast cancer – are prone to spread regionally to the lymph nodes because tumor cells travel and can metastasize via the lymph channel in the vicinity of the initial tumor. Lymphatic drainage scintigraphy using the Symbia SPECT/CT system (Single Photon Emissions Computed Tomography / Computed Tomography) enables the tracking of sentinel lymph nodes using radioactively marked substances that concentrate in them. Precise localization of these lymph nodes is possible even in complex locations because the anatomic landmarks can be displayed in a CT scan. Laboratory analysis of these sentinel lymph nodes can eliminate the need to remove all axillary lymph nodes, and the resulting complications, for many patients.
The newest system from Siemens – the Biograph mCT molecular computed tomography system – helps in providing a precise cancer diagnosis. The system can be used in both radiology and nuclear medicine and is suited for PET/CT (Positron Emissions Tomography) as well as pure CT examinations. Various biomarkers help here in localizing remote metastases in bones and other tissue, supporting the physician in more precisely planning the follow-up therapy.
Therapy monitoring – advances in immune diagnostics
More recent developments in immune diagnostics have resulted in a biomarker that can support the physician in selecting from a wide range of medications – especially when dealing with metastases. The concentration of this biomarker, known as HER-2/neu, is determined in the patient’s blood. HER-2/neu is an oncoproteine that plays a key role in an aggressive form of cancer. The assay for HER-2/neu in serum from Siemens Diagnostics is for determining HER-2/neu protein in the blood of patients with metastasizing breast cancer. The HER-2/neu values measured over the course of the disease provide valuable information regarding the course of therapy and the patient’s response to therapy. This enables the treating physician to adjust the therapy as required. Additionally, the serum assay provides information on the prognosis of the disease.
19.05.2010
- breast cancer (629)
- breast imaging (128)
- display (438)
- elastography (89)
- imaging (1645)
- medical technology (1555)
- molecular (205)
- MRI (836)
- ultrasound (769)