The usefulness of musculoskeletal MRI
A report by Thomas H Magee.
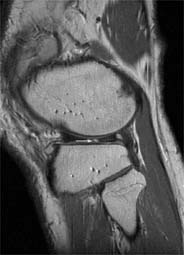
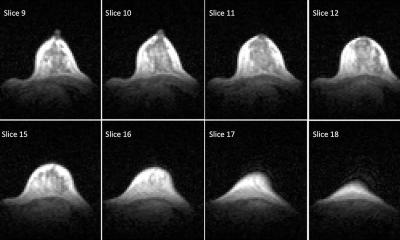
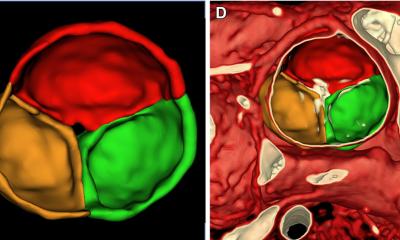
The inherent soft tissue contrast and high spatial resolution of MRI available on high field scanners allows for very accurate diagnoses. Musculoskeletal also has been useful for determining the extent of disease in soft tissue and bony tumours - often not well seen on conventional radiograph or a CT scan. Often, a bone scan can demonstrate increased radiotracer uptake in such cases, but lacks the specificity of MRI. A bone scan will demonstrate increased uptake in trauma, infection or tumour. MRI will demonstrate very specific findings in tumours that help differentiate them from trauma or infection.
MR is useful in demonstrating the presence and extent of infection, which helps guide the right course of action in treating infections. The treating physician is better able to determine whether surgery will be beneficial or whether the infection can be treated with antibiotics only.
Overall we have found MR to be a highly accurate non-invasive diagnostic test for early and specific diagnosis of many types of musculoskeletal disease, and this has significantly improved the treatment of patients with many types of musculoskeletal disease.
02.08.2006