Image source: Qure.ai
News • AI-assisted diagnostics
Two Dutch hospitals implement AI for lung nodule detection on chest X-rays
Catharina Ziekenhuis and UMC Utrecht integrate Qure.ai software into radiology workflows
Two major Dutch hospitals, Catharina Ziekenhuis in Eindhoven and University Medical Center (UMC) Utrecht, are integrating artificial intelligence (AI) from Qure.ai into their chest X-ray workflows. The goal is to support earlier and more consistent detection of potentially cancerous lung nodules.
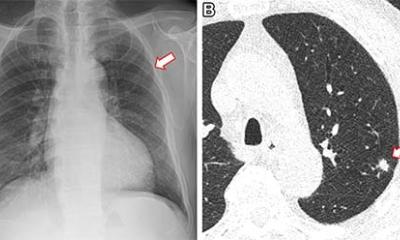
Both hospitals are adopting AI-enabled lung nodule programs to establish opportunistic screening pathways. The approach aims to detect lung cancer earlier and reduce variation in referral decisions across different experience levels. Qure.ai's chest X-ray solution, qXR, flags subtle nodules to assist radiologists - even when patients are scanned for unrelated reasons.
By integrating this AI program into our workflow, we can significantly enhance our ability to detect subtle lung nodules, which is paramount for the early diagnosis of lung cancer
Firdaus Mohamed Hoesein
UMC Utrecht, one of the Netherlands' largest university hospitals, combines academic research with clinical practice. The hospital has an established scientific track record in radiological aspects of lung cancer and AI. As an academic institution with a teaching mandate, it also prepares future clinicians to work with AI-enabled diagnostics.
Dr. Firdaus Mohamed Hoesein, Thoracic Radiologist and AI expert at UMC Utrecht, says: "AI-enabled diagnostics in radiology are an important tool for today's radiology practice. By integrating this AI program into our workflow, we can significantly enhance our ability to detect subtle lung nodules, which is paramount for the early diagnosis of lung cancer. This initiative directly aligns with our mission to find lung cancer at earlier stages and improve patient outcomes."
Dr. Joost Nederend, Radiologist at Catharina Ziekenhuis, adds: "There is growing evidence that AI can improve detection rates without compromising - and potentially even improving - the positive predictive value for referrals. It can also be valuable in supporting consistent decision-making, especially when chest X-rays are interpreted by radiologists from different subspecialties, those in the earlier stages of their careers, or residents in training."
Image source: Qure.ai
Catharina Ziekenhuis is a public tertiary care hospital with capabilities to treat lung cancer. A large share of its chest X-rays originates from general practitioner referrals for symptoms such as persistent cough.
Earlier this year, Erasmus Medical Centre in Rotterdam extended its collaboration with Qure.ai by initiating a chest X-ray AI study.
Bhargava Reddy, Chief Business Officer, Oncology at Qure.ai, says: "Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, including in the Netherlands. To fight back, we need to shift the focus to early detection. Specialist healthcare AI can accelerate this transformation by acting as a tireless second set of eyes, spotting small lung nodules on X-rays that might otherwise be missed. At the same time, it builds knowledge and know-how that drive clinical, operational, and economic value within hospitals and across health systems." He continues: "The momentum in the Netherlands is unmistakable. From Erasmus Medical Centre to Catharina Ziekenhuis and UMC Utrecht - institutions are confidently deploying AI that both elevates clinical standards and aims to future-proof Dutch healthcare."
Source: Qure.ai
09.12.2025