MR-guided radiotherapy
Real-time image guidance during radiation therapy could prove the ultimate means to ramp tumour targeting accuracy and enable real-time tracking of moving targets. MR imaging enables precise soft-tissue visualization with no additional ionizing radiation exposure. Unfortunately, MR systems and linear accelerators are inherently incompatible and some innovative design work is required for them to operate in tandem.

Despite the technical obstacles, there are a few research teams around the world developing such systems, including, for example, the Linac-MR research group at the Cross Cancer Institute in Edmonton, Canada. Here, researchers are merging the imaging capabilities of an MRI system with the treatment capabilities of a linac. And last month, the group demonstrated that the prototype system can successfully perform MR imaging during irradiation.
"The resultant image is comparable to that obtained without irradiation," explained Gino Fallone, professor and director of medical physics at the Cross Cancer Institute/University of Alberta. "This, we believe, is the first ever real-time MR image obtained of an object undergoing 6 MV irradiation."
The hybrid device comprises a 6 MV linac mounted on the open end of a biplanar, low-field (0.2 T) MRI magnet, with both the linac and magnet sited on a single gantry that rotates around the patient. The system is based upon a rotating-biplanar geometry, in which the magnetic field vector is fixed with respect to the incident photon-beam direction as the gantry rotates. The current prototype - designed for image-guided radiotherapy of the brain - has a 27 cm opening, large enough to accommodate a head. The team has also begun work on a whole-body system that has a 70 cm opening between the planes.
The design of the system minimizes the effect of the magnetic field upon the dose distribution and, in cases where small dose perturbations are unavoidable (such as lung treatments), enables correction via a simple algorithm. Interference from the linac's RF field upon the MR apparatus, meanwhile, is avoided using "an appropriate design that must be considered confidential at the moment," according to Fallone.
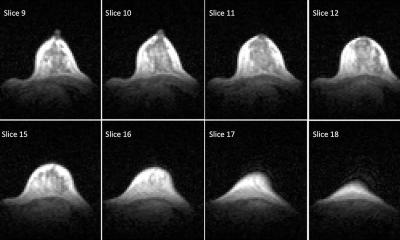
In a proof-of-concept test, Fallone and co-workers used the prototype to record images of an acrylic phantom before and during linac irradiation. The phantom comprised a rectangular cube containing holes of 2.52, 3.45 and 4.78 mm in diameter and immersed in a copper sulphate solution. Images recorded during 6 MV irradiation did not show any significant distortions and were similar to those obtained prior to irradiation, with just a small difference in the signal-to-noise ratios (see figure).
The group has submitted a major scientific grant application to the Canada Foundation for Innovation and the Alberta Science and Research Investments Program to develop the whole-body system for use in clinical research. "Depending on the funding, clinical trials may start within one to five years," Fallone told medicalphysicsweb.
Source: Medical Physics Web
28.01.2009