News • Work in Progress
Toshiba Medical pushes the boundaries of automation
Automation might be the solution for many of the challenges radiologists and clinicians face today. Toshiba Medical, a Canon Group, is currently pushing the boundaries of what automation can accomplish and presenting their project in progress at this year's RSNA.
Automated Insights
Overwhelming volume of clinical data every day, limited access to relevant clinical information, missed findings and lack of consistent follow-up are among the most urgent challenges radiologists and clinicians face today. Automated Insights, a tool developed by Toshiba Medical, is designed to overcome these hurdles.
Automated Insights uses machine learning to help you at every step in the process of caring for your patients so that you can work more efficiently and provide better care to your patients. It can help indicate:
- Which study should be read next
- Patient identification
- What actionable findings the study contains
- What should be done next to care for the patient
Algorithms operate, learn and improve continuously. They can even learn from other algorithms deployed at different institutions. As soon as new patient data or results become available, they can be run automatically.
Prioritization
Every study needs to be read, but some studies are more urgent than others. Automated Insights is designed to help you prioritize your worklist by automatically prescreening new studies as they arrive.
Clinical Context
Time is often wasted searching the EMR to obtain clinical context. Without enough clinical context, it’s more difficult to interpret studies effectively, and that can potentially change diagnoses. Automated Insights is designed to automatically fetch and summarize relevant information so that you understand each patient well enough to provide the best possible care.

Actionable Findings
Having to read even more images in more studies — as well as prior studies and reports — can be overwhelming. And fatigue, stress, interruptions and distractions can result in missed actionable findings.
Automated Insights is designed to help you reduce missed findings.

Follow-up Management
Focus on caring for your patients while being assured that everyone understands which actions should be taken, who is responsible for taking those actions, and when those actions should be taken. In a busy environment, ensuring that actionable findings are acted upon correctly can be challenging. Automated Insights is designed to identify actionable findings and follow-up recommendations and tracks them to ensure that they are acted upon in the most appropriate manner by the most appropriate clinician.
Close the Loop
Your system can become smarter over time. Automated Insights continuously learns and refines its findings, predictions, and recommendations with each new result that it produces.
Improving the Future of Healthcare
In continuing to develop solutions that incorporate forward-thinking ideas such as automated insights, we help healthcare organizations stay at the forefront of productivity, resource usage and patient outcomes.
NOTE: Automated Insights is a work in progress
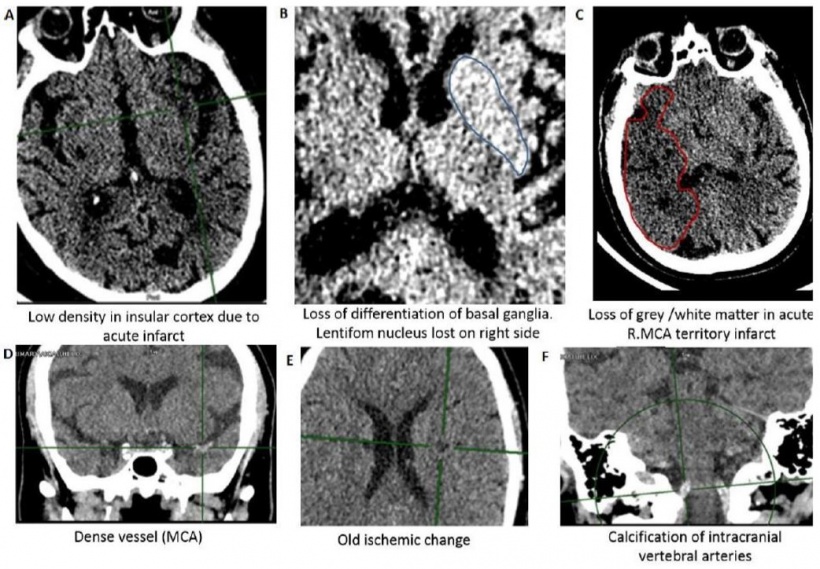
Automated Stroke Sign Detection and ASPECTS in Non-Contrast CT Brain Scans
Another field where automation can be used is the detection of early ischemic damage in Non-Contrast-CT (NCCT). To achieve this, an ASPECT score is estimated for each patient from the location and size of early ischemic changes. This score is thence used to support decision making, especially for challenging diagnoses.
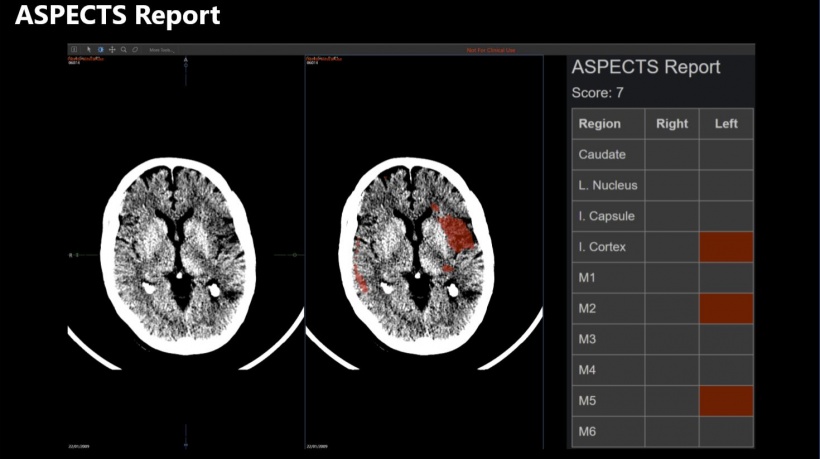
ASPECTS [Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score] is a scoring system to indicate the severity of brain ischemia. The brain volume supplied by the middle cerebral artery is divided into ten territories per hemisphere and each territory is scored as presenting ischemic signs or not. The score starts at ten – representing no ischemic regions – and reduces by one for each affected territory in the symptomatic hemisphere.
ASPECTS correlates with patient outcome and is one of a number of factors used to determine treatment options for a stroke patient.
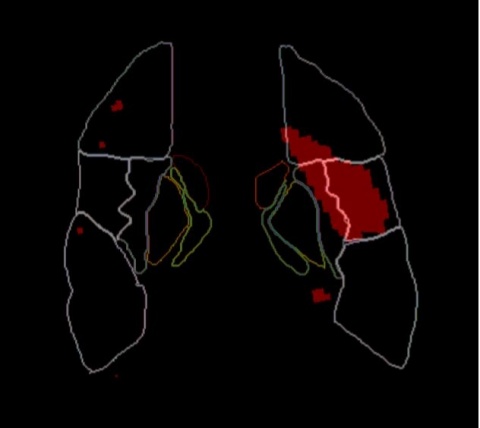
If the stroke is identified sufficiently early, ischemic stroke patients are treated via IV thrombolysis or mechanical thrombectomy.This treatment relies on ruling out haemorrhagic stroke and classifying the stroke severity.
However, signs of early ischemic change in NCCT can be challenging to detect. The initial hours from symptom onset are critical to a positive patient outcome. NCCT is often the first scan taken of a patient with suspected stroke so it is crucial to identify early stroke signs in these scans to enable correct and timely treatment.
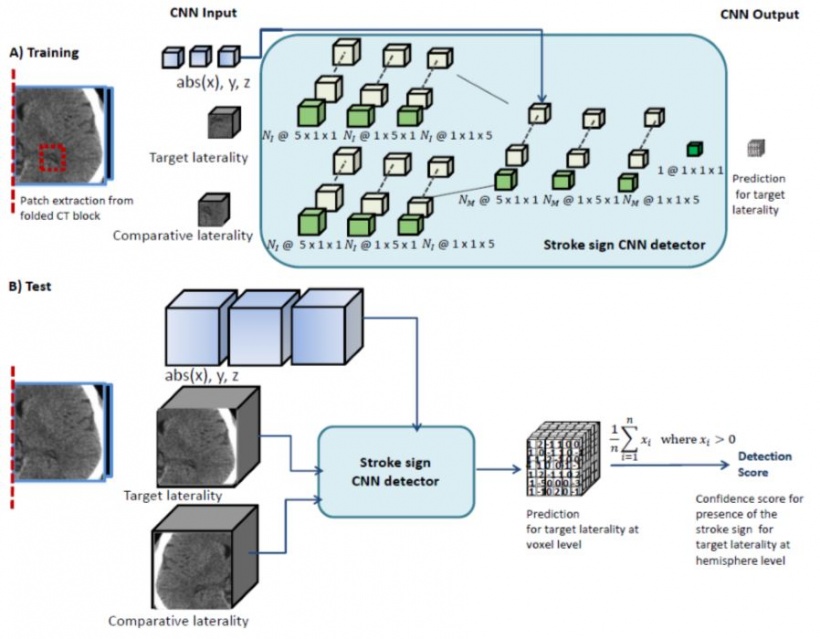
Toshiba Medical Visualization Systems in Edinburgh, UK, obtained acute NCCT scans for 170 patients with suspected acute ischemic stroke within 6 hours of onset from the Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, Glasgow. An in-house clinical expert under the supervision of an experienced neuroradiologist developed ground truth for dense vessel and ischemia for all datasets by slice level manual segmentation.
They use a symmetry-exploiting convolutional neural network (CNN) that is sensitive to differences between brain hemispheres to learn areas where early stroke signs present. The two brain hemispheres and an anatomical atlas are input, and a voxel wise detection volume is output.
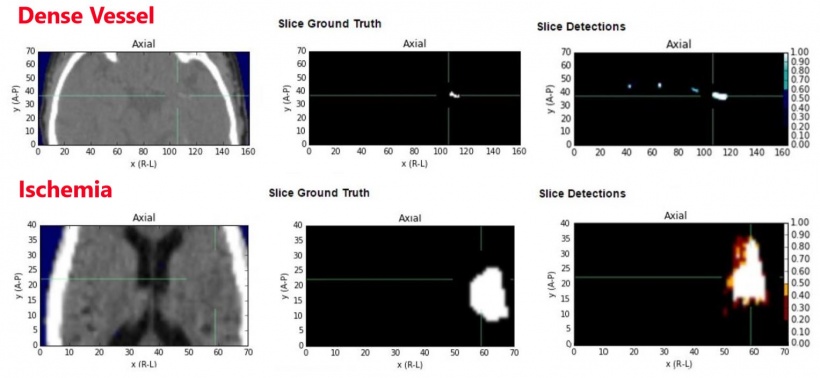
Results
| Ischemia | Dense Vessel | |
| ROC (Area Under Curve) | 0.915 | 0.964 |
| Precision-Recall (Area Under Curve) | 0.783 | 0.898 |
| ASPECTS (Dichotomised >=7) | Cohen's Kappa = 0.58 |
Conclusions
- Early detection of dense vessels and ischemia in NCCT informs treatments
- A symmetry exploiting CNN can detect these early signs.
- Stroke severity can be assessed by ASPECTS, calculated from ischemic region detection overlaid on a vascular atlas.
Source: Toshiba Medical, a Canon Group
30.11.2017