Stroke Imaging: The Procedure in Practice
In the past, native computed tomography of the neurocranium (CCT) was often the only procedure to diagnose a stroke. Technical limitations of previous generations of scanners made their use impractical for complementary methods of visualising blood
vessels or for perfusion imaging. With the introduction of multi-slice spiral CT these technical limitations disappeared and both perfusion CT (PCT) and CT angiography (CTA) have evolved. In the field of stroke diagnosis these developments have led to the introduction of what is known as stroke imaging. Modern CT protocols for diagnosing a stroke, consisting of the basic techniques of CCT, PCT and CTA,
allow a comprehensive evaluation of the the cervico-cerebral vessels and perfusion status from the very first imaging procedure, so that a treatment decision can be made rapidly. The following article briefly describes some practical aspects of carrying out and evaluating stroke imaging.
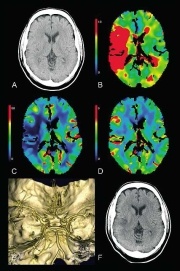
MTT parameter image (B) comprises approx. 2/3 of the territory of the middle cerebral artery. According to the CBF parameter
image (C), blood flow is reduced in the cortex, particularly in the insular cortex.
In the CBV parameter image (D) a slight reduction in blood
volume can only be observed in the operculo-insular cortex,
otherwise CBV is increased in the cortex due to auto-regulation.
The cause was found in the CTA(E) to be occlusion in the distal
M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery. As there was a
widespread infarct penumbra according to PCT criteria and no
contraindications, intravenous thrombolysis was indicated. After
successful lysis only a small insular partial middle cerebral artery
infarct could be observed on the control image for the procedure
(fig. modified according to [7]).
This article was first published in the VISIONS, issue 9/2006, a publication of Toshiba Medical Systems
03.07.2007