Philips forecasts advances for healthcare in 2020
Previewing technologies that may be in use in about a decade, Philips Healthcare recently introduced us to researchers who discussed their many current and ongoing projects.
Magnetic Particle Imaging - MPI uses the magnetic properties of injected iron-oxide nanoparticles to measure the concentration in blood. Because the human body contains no naturally occurring magnetic materials visible to MPI, there is no background signal. After injection, the nanoparticles appear as bright signals in the images, from which the concentrations can be calculated. By combining high spatial resolution with short image acquisition times (as short as 1/50th of a second), MPI can capture dynamic concentration changes as the nanoparticles are swept along in the blood stream. This effect allows MPI scanners to perform a wide range of functional cardiovascular measurements in one single scan. Measurements of coronary blood supply, myocardial perfusion, and the heart’s ejection fraction, wall motion and flow speeds can then be done within one scan.
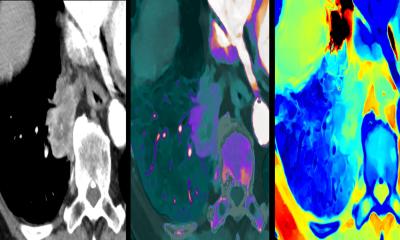
Cardiac Modelling - Accurately recognising organ structures from X-ray CT and MRI scans takes years of training and experience. Retaining that information is doubly difficulty when carrying out delicate minimally-invasive surgery (MIS).
The scientists have recently been using image recognition techniques to locate landmarks and identify the boundaries between different types of tissue. Patient-specific 3-D heart models from X-ray CT scans have been produced that automatically segment out all four heart chambers (the left and right atria and ventricles). This should enable radiologists to visualise hearts more easily, as well as enable automated extraction of important clinical information, such as chamber volumes. Overlaid on to real-time X-ray fluoroscopy images from Philips Medical Systems’ EP (Electrophysiology) Navigator Workstation, these models already help physicians to navigate catheters when performing minimally invasive cardiac surgery.
Sonodrugs - Powerful drugs to treat certain types of cancer and cardiovascular diseases are mostly administered intravenously or orally and allow only limited control over the distribution of medication in the body, circulating in the bloodstream and interacting with diseased and healthy tissues and organs.
The Sonodrugs project aims to develop drug delivery vehicles that can be tracked by ultrasound or MRI and triggered by ultrasound to release the medication at the desired location. Controlled drug delivery will increase therapeutic efficiency and minimise side effects, as well as individualise therapy.
Heart Failure Management - HF patients frequently suffer complications that currently result in hospitalisation. These complications are typically the result of a process known as decompensation, in which progressive deterioration leads to potentially lethal conditions, such as fluid accumulation in the lungs. In many cases decompensation remains undetected until the patient suffers noticeable symptoms and visits the doctor.
As part of the MyHeart initiative, Philips Research is developing an advanced HF management system that aims to provide several days advance warning of life-threatening decompensations, giving doctors time to stabilise the condition by modifying the patient’s drug regime, rather than having to admit them to hospital.
01.09.2009