Video • Adaptation to oxygen availability
Nobel Prize in Medicine goes to William G. Kaelin Jr, Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, and Gregg L. Semenza
The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly to William G. Kaelin Jr., Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe and Gregg L. Semenza for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.
Animals need oxygen for the conversion of food into useful energy. The fundamental importance of oxygen has been understood for centuries, but how cells adapt to changes in levels of oxygen has long been unknown. William G. Kaelin Jr., Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe and Gregg L. Semenza discovered how cells can sense and adapt to changing oxygen availability. They identified molecular machinery that regulates the activity of genes in response to varying levels of oxygen.
The seminal discoveries by this year’s Nobel Laureates revealed the mechanism for one of life’s most essential adaptive processes. They established the basis for our understanding of how oxygen levels affect cellular metabolism and physiological function. Their discoveries have also paved the way for promising new strategies to fight anemia, cancer and many other diseases.
Oxygen, with the formula O2, makes up about one fifth of Earth’s atmosphere. Oxygen is essential for animal life: it is used by the mitochondria present in virtually all animal cells in order to convert food into useful energy. Otto Warburg, the recipient of the 1931 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, revealed that this conversion is an enzymatic process.
During evolution, mechanisms developed to ensure a sufficient supply of oxygen to tissues and cells. The carotid body, adjacent to large blood vessels on both sides of the neck, contains specialized cells that sense the blood’s oxygen levels. The 1938 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Corneille Heymans awarded discoveries showing how blood oxygen sensing via the carotid body controls our respiratory rate by communicating directly with the brain.
In addition to the carotid body-controlled rapid adaptation to low oxygen levels (hypoxia), there are other fundamental physiological adaptations. A key physiological response to hypoxia is the rise in levels of the hormone erythropoietin (EPO), which leads to increased production of red blood cells (erythropoiesis). The importance of hormonal control of erythropoiesis was already known at the beginning of the 20th century, but how this process was itself controlled by O2 remained a mystery.
Recommended article

News • Low Oxygen, High Risk
How tumors adapt to become more aggressive
One of the many reasons tumors are so difficult to treat is that they are able to adapt whenever they are exposed to unfavorable conditions. Hypoxia, or a lack of oxygen, is one example of a phenomenon that should weaken the tumor, but instead, the malignant cells are able to compensate and drive more aggressive disease behavior.
Gregg Semenza studied the EPO gene and how it is regulated by varying oxygen levels. By using gene-modified mice, specific DNA segments located next to the EPO gene were shown to mediate the response to hypoxia. Sir Peter Ratcliffe also studied O2-dependent regulation of the EPO gene, and both research groups found that the oxygen sensing mechanism was present in virtually all tissues, not only in the kidney cells where EPO is normally produced. These were important findings showing that the mechanism was general and functional in many different cell types.
Semenza wished to identify the cellular components mediating this response. In cultured liver cells he discovered a protein complex that binds to the identified DNA segment in an oxygen-dependent manner. He called this complex the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) . Extensive efforts to purify the HIF complex began, and in 1995, Semenza was able to publish some of his key findings, including identification of the genes encoding HIF. HIF was found to consist of two different DNA-binding proteins, so called transcription factors, now named HIF-1α and ARNT. Now the researchers could begin solving the puzzle, allowing them to understand which additional components were involved and how the machinery works.
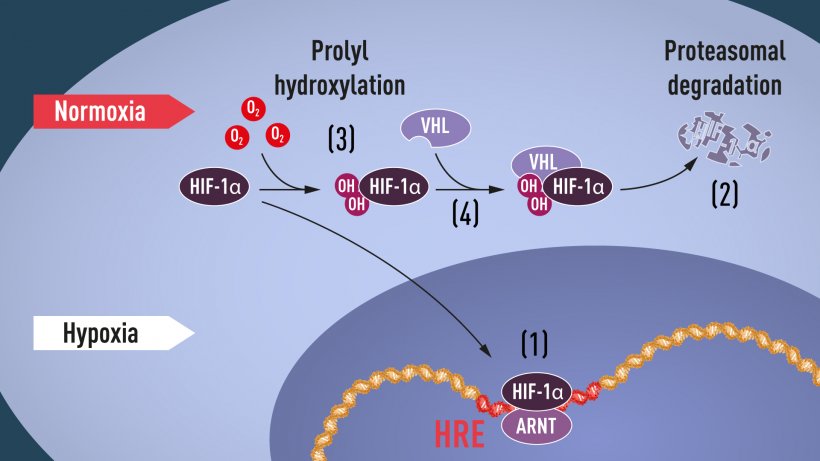
Illustration: © The Nobel Committee for Physiology or Medicine. Illustrator: Mattias Karlén
When oxygen levels are high, cells contain very little HIF-1α. However, when oxygen levels are low, the amount of HIF-1α increases so that it can bind to and thus regulate the EPO gene as well as other genes with HIF-binding DNA segments (Figure 1). Several research groups showed that HIF-1α, which is normally rapidly degraded, is protected from degradation in hypoxia. At normal oxygen levels, a cellular machine called the proteasome, recognized by the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin Rose, degrades HIF-1α. Under such conditions a small peptide, ubiquitin, is added to the HIF-1α protein. Ubiquitin functions as a tag for proteins destined for degradation in the proteasome. How ubiquitin binds to HIF-1α in an oxygen-dependent manner remained a central question.
The answer came from an unexpected direction. At about the same time as Semenza and Ratcliffe were exploring the regulation of the EPO gene, cancer researcher William Kaelin, Jr. was researching an inherited syndrome, von Hippel-Lindau’s disease (VHL disease). This genetic disease leads to dramatically increased risk of certain cancers in families with inherited VHL mutations. Kaelin showed that the VHL gene encodes a protein that prevents the onset of cancer. Kaelin also showed that cancer cells lacking a functional VHL gene express abnormally high levels of hypoxia-regulated genes; but that when the VHL gene was reintroduced into cancer cells, normal levels were restored. This was an important clue showing that VHL was somehow involved in controlling responses to hypoxia. Additional clues came from several research groups showing that VHL is part of a complex that labels proteins with ubiquitin, marking them for degradation in the proteasome. Ratcliffe and his research group then made a key discovery: demonstrating that VHL can physically interact with HIF-1α and is required for its degradation at normal oxygen levels. This conclusively linked VHL to HIF-1α.
Recommended article
News • Therapy-resistant cells
Von Hippel-Lindau: How to kill hereditary cancer
Researchers identified how to kill therapy-resistant cells in hypoxic tumors and in cells arising in the von Hippel-Lindau hereditary cancer. In a recent publication in PNAS, the research group identified how to kill therapy-resistant cells in hypoxic tumors and in cells arising in the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) hereditary cancer.
Many pieces had fallen into place, but what was still lacking was an understanding of how O2 levels regulate the interaction between VHL and HIF-1α. The search focused on a specific portion of the HIF-1α protein known to be important for VHL-dependent degradation, and both Kaelin and Ratcliffe suspected that the key to O2-sensing resided somewhere in this protein domain. In 2001, in two simultaneously published articles they showed that under normal oxygen levels, hydroxyl groups are added at two specific positions in HIF-1α (Figure 1). This protein modification, called prolyl hydroxylation, allows VHL to recognize and bind to HIF-1α and thus explained how normal oxygen levels control rapid HIF-1α degradation with the help of oxygen-sensitive enzymes (so-called prolyl hydroxylases). Further research by Ratcliffe and others identified the responsible prolyl hydroxylases. It was also shown that the gene activating function of HIF-1α was regulated by oxygen-dependent hydroxylation. The Nobel Laureates had now elucidated the oxygen sensing mechanism and had shown how it works.
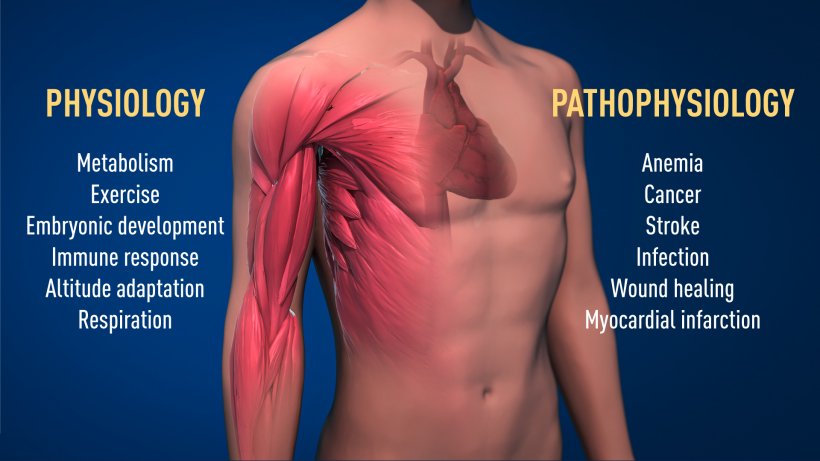
Illustration: © The Nobel Committee for Physiology or Medicine. Illustrator: Mattias Karlén
Thanks to the groundbreaking work of these Nobel Laureates, we know much more about how different oxygen levels regulate fundamental physiological processes. Oxygen sensing allows cells to adapt their metabolism to low oxygen levels: for example, in our muscles during intense exercise. Other examples of adaptive processes controlled by oxygen sensing include the generation of new blood vessels and the production of red blood cells. Our immune system and many other physiological functions are also fine-tuned by the O2-sensing machinery. Oxygen sensing has even been shown to be essential during fetal development for controlling normal blood vessel formation and placenta development.
Oxygen sensing is central to a large number of diseases (Figure 2). For example, patients with chronic renal failure often suffer from severe anemia due to decreased EPO expression. EPO is produced by cells in the kidney and is essential for controlling the formation of red blood cells, as explained above. Moreover, the oxygen-regulated machinery has an important role in cancer. In tumors, the oxygen-regulated machinery is utilized to stimulate blood vessel formation and reshape metabolism for effective proliferation of cancer cells. Intense ongoing efforts in academic laboratories and pharmaceutical companies are now focused on developing drugs that can interfere with different disease states by either activating, or blocking, the oxygen-sensing machinery.
Source: The Nobel Committee/Nobel Media AB
07.10.2019