ESC Congress 2015
Biotronik presents its CRT-Ds approved for full-body MRI scanning
Biotronik, manufacturer of MR conditional cardiac devices, has announced CE approval for full-body MRI scanning for its last two generations of ProMRI cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator* (CRT-Ds) systems.
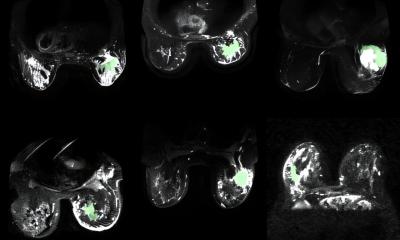
Biotronik now offers CRT-D patients access to full-body MRI scans, the gold standard in soft tissue imaging. Since 2013, it has had CRT-Ds approved for MRI scanning with an exclusion zone, now expanded to give these patients access to full-body MRI scanning at 1.5 tesla strength.
“This is a great development, especially in the treatment of heart failure (HF) patients, and opens diagnostic capabilities these patients were previously denied,” commented Dr. Albert C. van Rossum from VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. “CRT-Ds are commonly implanted in patients with severe heart problems, often the result of a heart attack. For the first time, we now have the opportunity to use the unique benefits of MRI to examine in depth how the heart reacts to resynchronization therapy and adjust treatments if needed. Full-body MRI including the heart during resynchronization therapy will give these patients a huge advantage, as it provides physicians much more detailed insight of their complex heart condition.”
HF patients often have comorbidities such as stroke, which is best diagnosed through an MRI. “In Europe alone, heart failure affects at least 15 million people.1 It is a huge patient population and the chances of them needing a device or an MRI, or both, are high. That is why we make patient access to MRI scanning one of our top priorities,” stated Manuel Ortega, Senior Vice President of BIOTRONIK. “With CE approval of our last two generations of ProMRI CRT-Ds for full-body scanning, we broaden the options for physicians and patients, enabling optimal treatment.”
For more information, visit: www.biotronik.com or Visit the Biotronik booth at ESC 2015, August 29th – September 2nd, Exhibition Hall #H600
Reference
1 Dickstein K et al. European Heart Journal. 2008, 29
26.08.2015