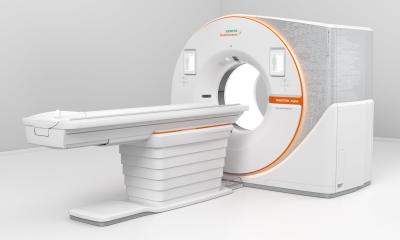
Siemens: heart scan with lower dosage by using DSCT
A new study reveals that, with dual-source computed tomography (DSCT), the effective dosage for a heart examination can be significantly lowered, in comparison to conventional computed tomography (CT). The study also demonstrated that stenoses can be diagnosed with the same high accuracy as with invasive x-ray angiography.
Angiography is a diagnostic procedure used to clarify coronary arterial occlusion. Normally, this examination is conducted using angiography devices in the catheter laboratory and computed tomographs (CT), but with CT, the question of the radiation dosage plays a huge role. Researchers at the University Hospital in Zürich wanted to know whether the dose used during CT angiography can be reduced. The research team examined 120 patients with suspected coronary heart disease in a Somatom Definition from Siemens, the world's first computed tomograph with two x-ray tubes. The results of the study were published in the June issue of "Heart", the official journal of the British Cardiovascular Society.
"The results show that CT coronary angiography with a dual-source CT in step-and-shoot mode produces images of excellent diagnostic quality in patients with stable heart rates up to 70 bpm. The dosage reduction achieved in comparison to previous CT angiography is also remarkable. In our study, we required an effective dose of 2.5 mSv on average with a deviation of plus/minus 0.8 mSv. In the literature, a normal average effective dose for heart scans of between 9 and 21 mSv is reported," said Dr. Hatem Alkadhi, specialist in Radiology at the Institute for Diagnostic Radiology, University Hospital Zürich, Switzerland.
The Adaptive Cardio Sequence supplements the step-and-shoot method with intelligent algorithms, which monitor the heart frequency of patients and, if necessary, respond to arrhythmia, such as extrasystoles, additional heart beats. In this case, the recording phase is automatically postponed in order to avoid image errors due to the sudden movement. In addition, the recording window can be widened a little more if required so that, with the Adaptive Cardio Sequence, the robustness of the CT scan can be increased significantly overall.
"For Siemens, the safety of the patients has always been the primary focus of the developments in CT. At the same time, we consider our highest obligation to be to give doctors the best diagnostic image quality and to support them in making their workflow as efficient as possible. With this outlook and constant further development, Siemens has positioned itself as the market leader in CT technology," said Dr. Sami Atiya, CEO, at Computed Tomography, Siemens Healthcare. "Innovations for dose reduction in conjunction with improved diagnostic image quality, are therefore of the utmost importance to us. This is why we have also further developed our Adaptive Cardio Sequence, now for the dual-source CT. The study from Zürich confirms to us that the combination of step-and-shoot and dual-source computed tomography does significantly reduce the dosage required during heart scans."
This article is adapted from the original press release.
26.08.2008