Dual Energy
Siemens - Dual Energy to routine CT Imaging
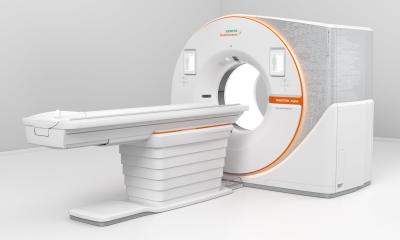
With the new version of the Somatom Definition Edge, Siemens Healthcare has created the basis for establishing the dual energy procedure in clinical routine. The innovative X-ray tube concept in the new CT scanner, enables simultaneous imaging at two different energy levels for the first time in single source computed tomography.
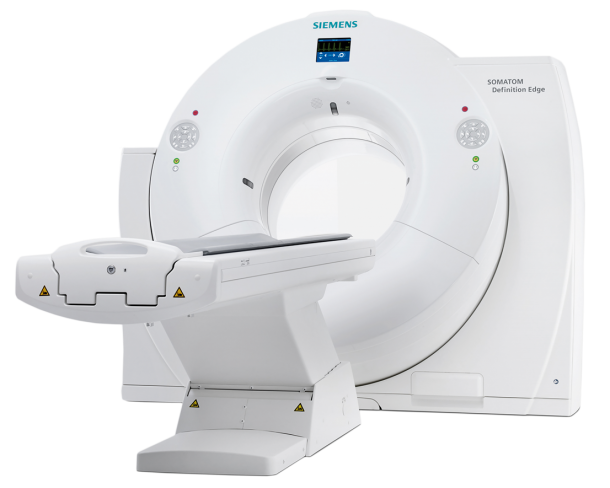
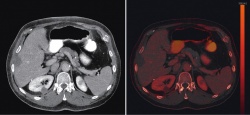
Thanks to a novel user- and patient-friendly measurement method, information on tissue and other material can be obtained as well as traditional morphological data, even during examinations with high contrast media dynamics. This means that more patients will benefit from the added value of dual energy imaging.
Single Source Dual Energy – how it works
In dual energy imaging, the same region of the body is examined using two different energy levels. The two datasets offer more detailed information about tissue composition that goes beyond pure morphology. For instance, metal artifacts caused by implants such as artificial hips are reduced considerably, while tissue and bone structures can be displayed more clearly. However, in cases where data have been acquired using fast kV-switching or dual layer detector technology – dual energy imaging involved significant drawbacks. Single source dual energy images acquired with these methods were excluded for many important radiological use cases, because the tube does not emit the two energy spectra at the same time, only in succession through rapid switching or through spectra separation at the detector side after penetrating the patient. With kV-switching, the segmentation of the measuring points significantly impairs the image quality due to the limited data per energy level. At the same time, increased X-ray doses are inevitable because the dose cannot be modulated to reduce radiation.
New source design splits the X-Ray Beam into two energy spectrums
Not so with the TwinBeam Dual Energy technology from Healthcare, in which the X-ray beam emitted is split into two different energy spectra before reaching the patient thanks to an innovative tube design. This means that the Somatom Definition Edge generates the dual energy images at the same time.
The benefits of the new procedure are illustrated by the diagnostics in a case of suspected pulmonary embolism: Due to the improved tissue differentiation and the precise representation of contrast media distribution, vascular occlusions can be quickly identified and their size determined.
In addition to increasing the diagnostic strength of clinical images, TwinBeam technology also minimizes the X-ray dose required in a different way to other single source dual energy procedures. All dose-reducing Siemens technologies can be used with the Somatom Definition Edge. This now also includes Admire, the model-based iterative reconstruction procedure which was just recent released on the Somatom Force and whose scanner-specific algorithms can reduce X-ray doses further still – achieving excellent image resolution and extremely low image noise even at low doses.
Iterative metal artifact reduction for clearer material differentiation
To further improve not only the quality of dual energy examinations, but also of conventional CT scans, Siemens Healthcare is additionally introducing a new iterative algorithm for metal artifact reduction with the new Somatom Definition Edge: iMAR. This allows respective artifacts – caused by implants, artificial joints or pacemakers – to be reduced significantly. Such artifacts may lead in the worst case to non-diagnostic images by concealing the relevant pathologies.
Even if a radiologist wishes to check whether bone fractures have healed and metal objects such as screws and plates can be removed, the iMAR algorithm can be used to clearly assess the anatomical details in the area of transition between bone and metal. With the aid of iMAR, streak artifacts can, for instance, be significantly reduced in clinical images, according to first scientific results.
The products / features (here mentioned) are not commercially available in all countries. Due to regulatory reasons their future availability cannot be guaranteed. Further details are available from the local Siemens organizations.
For more information, please visit www.siemens.com/healthcare
03.03.2015