Heart-Rate Adaptive CT Image Reconstruction
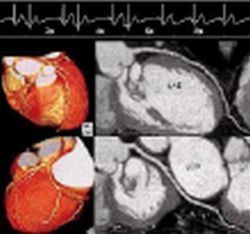
The advent of multislice computed tomography has made coronary artery imaging with computed tomography (CT) a clinical reality. When a CT scanner with 16 detector rows is used, scan times are within the breathholding capabilities of most patients. The latest generation of CT scanners with 64 detector rows has reduced the scan time to 6-10 seconds, which is suitable for examining all but the most severely ill patients. The objective of this newly developed enhanced algorithm for multisegment image reconstruction in diagnostic cardiac computed tomography is to maintain constant image quality over the entire range of clinically relevant heart rates, i.e. from 50 to 140 beats per minute (bpm). Image reconstruction drawing on the raw data of up to five segments from consecutive cardiac intervals improves the theoretical temporal resolution to 35 ms. Numerous studies in cardiac diagnostics employing the basic version of multisegment image reconstruction with and without administration of a beta blocker have been published to date . For motion-free cardiac imaging, the basic requirement in CT image reconstruction is high temporal resolution. The technical implementation of this requirement may follow several different approaches. The adaptive multisegment reconstruction technique is combined with a process by which the optimal systolic and diastolic phases are selected automatically (PhaseXact software).
This article was first published in the VISIONS, issue 11/2007, a publication of Toshiba Medical Systems
29.08.2007