Source: Shimadzu
Sponsored • Chemotherapy
5-FluoroUracil: Curing or killing the patient?
Fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapies are widely used, at least in the European area, for treating various types of cancer including digestive, breast, throat and brain cancer. Fluoropyrimidines are a group of anticancer drugs including the well-known 5-FluoroUracil (5-FU) and the prodrug capecitabine.
Fluoropyrimidine-based treatment can lead to severe toxicities or even lethal toxicity, but this is a rarely occurring state unless the patient suffers from a deficiency in the activity of the related enzyme involved in its metabolization, the so-called DPD or dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase. Administered intravenously, the Fluoropyrimidine molecule immediately undergoes intensive hepatic metabolism due to the action of the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase enzyme (DPD). Thus, only 10 percent of the administered dose is active. Since the active proportion is very low, doses administered are much greater than the usual dosages. It is therefore highly recommended to screen for partial or full deficiency of DPD to adjust the dose of 5-FU administered to patients.
In this context, beginning in 2018, the French agency regulating medicinal product safety ruled in favor of routine screening for DPD deficiency before treatment with fluoropyrimidine.
Several technologies are available on the market:
- Genotyping of the DPD gene has the advantage of producing a fast, relatively inexpensive and unambiguous response using automated techniques. Specificity is very good but sensitivity is relatively poor.
- Phenotyping is much more time-consuming with more complicated methods, difficulty of automation and a lower level of evidence.
- The indirect phenotypic technique, currently the most used, is the determination of overall DPD activity based on monitoring of the UH2/U ratio in plasma. This analysis uses sample extraction followed by separation in high performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry detection. This technique is faster and cheaper than the direct assay of activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Following an observation period, Haute Autorité de Santé (France) and INCa (Institute National du Cancer) recommend testing for DPD deficiency by determination of uracil plasma concentration [uracilemia] where fluoropyrimidine treatment is planned. The INCa statistics database estimated around 100.000 patients receiving fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy each year in France, increasing the need for a quick solution. This monitoring can be done by checking the ratio of dihydrouracil (UH2) to Uracil (U) and/or uracilemia using LC-MS/MS technology as mentioned earlier, and the criteria below are recommended.
Ratio UH2U | Prescription |
Between 3 and 4 | Standard dosage |
Between 2 and 3 | Warning: Dosage reduction not systematic |
Between 1 and 2 | Dosage reduced from 15 to 20% |
0,5 to 1 | Dosage reduced by 30% |
< 0,5 | Use not recommended |
Uracilemia | Prescription |
Below <16 ng/ml | Standard dosage |
≥ 16 ng/mL | Dosage reduced from 15 to 50%. |
>100 ng/ml | Use not recommended |
There have been numerous method developments around the world to analyze the UH2/U ratio by LC-MS/MS but all of them include complex sample preparation such as LLE (liquid-liquid extraction), centrifugation or SPE (solid phase extraction), making sample preparation both time-consuming and tedious.
The recent urge for systematic screening of all patients undergoing 5-FU treatment in France has placed laboratories under much pressure due to the low throughput of existing methods.
To cope with the situation, we propose a new solution based on the use of the CLAM-2030, a novel fully automated sample preparation system by Shimadzu, coupling a high-pressure liquid chromatography (NEXERA-X2, Shimadzu) and a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (LCMS-8060, Shimadzu).
Recommended article

Sponsored • Clinical Laboratory Automation Module
Highly flexible automated sample preparation module for LC-MS / MS
While IA’s (Immunoassay) has been the most used technic for clinical analysis, the shift to LC-MS / MS is constantly increasing for several type of analysis like immunosuppressant, vitamin D or steroids panel, but also for several new assays including anti-coagulants, antibiotics, plasma renin activity, etc. The change from Immunoassay to LC-MS / MS could have been faster if sample…
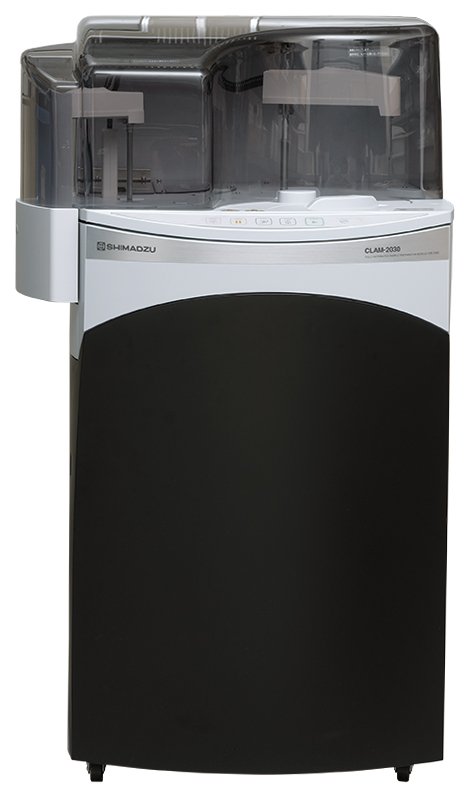

Launched in April 2016, the CLAM-2000 has already demonstrated its capabilities for automation prior to LC-MS/MS analysis in various fields such as clinical chemistry and toxicology. The new CLAM-2030 version improves reproducibility and accuracy of quantitation by implementation of new closed reagent vials as well as several hardware and software functionalities. The ability of the CLAM-2030 to draw sample from primary or secondary tube, and the capability for sample treatment with overlapping prior to analysis, allow quick sample pretreatment of less than 10 min including protein precipitation and fast LCMS quantitation of U and UH2 in 15 min. In addition, sample volume is low when compared to existing LCMS methods involving several extraction steps, reducing the burden for large blood sampling.
The methods developed (details currently under confidentiality agreement) easily reach an LOQ of 2,5 ng/ml for both U and UH2 compounds in plasma with good linearity for quantitation (r2>0,995). The method was developed with the aim of reaching the requirements of ISO 15189 in the department of Pharmacology and Toxicology of the Limoges University Hospital (France). In particular, the capability to quantify below or above the decision threshold (uracilemia at 16 ng/ml) was evaluated.
Source: Shimadzu; Author: Tiphaine ROBIN, PhD, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Limoges (partner of the Shimadzu Innovation Center)
17.05.2019