Fully digital X-ray based 3-D imaging drives MIS
In recent years, intra-operative 3-D C-arm imaging has revolutionised orthopaedics and trauma surgery. In particular using the images created during an operation, C-arms with 3-D capability can produce 3-D views of a quality effectively on a par with those of a CT scan.

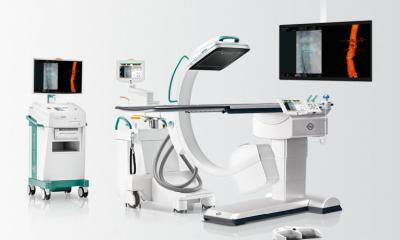
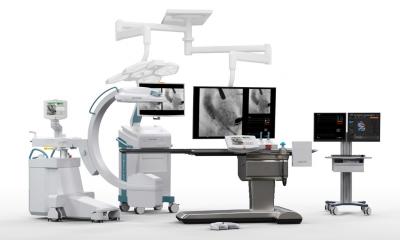
They allow improved intra-operative monitoring for the repositioning of complex fractures and insertion of implants. 3-D C-arms with flat panel detectors providing highly dynamic, distortion-free imaging have been on the market for barely two years. The image information is read out directly from the detector and becomes available in digital form immediately after acquisition. The use of digital flat panel detectors in mobile X-ray machines has significantly improved image quality and is opening up new fields of application in minimally invasive surgery (MIS).
Ziehm Imaging reports that it is leading the way in flat panel technology for mobile C-arms. In 2006, the company launched the Vision FD, the world’s first mobile C-arm with fully digital imaging. Furthermore, Ziehm’s flat panel technology has been implemented within the Ziehm Vision RFD mobile Intervention Suite and the Ziehm Vision FD Vario 3D. Vision RFD is particularly suitable for procedures in interventional radiology, neurosurgery, vascular surgery and cardiology, while Vision FD Vario 3D offers major advantages for traumatology, orthopaedics and brachytherapy. Using flat panel technology and a variable isocentre, the C-arm provides distortion-free intra-operative 3-D imaging which delivers critical additional information particularly for assessing complex fractures or during spinal operations.
Integrated navigation for greater operating theatre efficiency
New horizons in terms of precision and image quality are being opened up particularly by combining flat panel technology with navigation systems or Computer Assisted Surgery (CAS). Through direct connection to a navigation system, the intra-operative image data can be used directly for computer-assisted interventions.
Experience with using Ziehm Imaging’s flat panel technology has already been gained at the first orthopaedic spinal centre in Thiene (Vicenza) in north-eastern Italy, where trauma surgeons have been using the mobile C-arm Vision FD Vario 3D since December 2007. ‘We have used the C-arm as an intra-operative data source with good results. The system produces high quality images with high contrast resolution,’ said Dr. Balsano, head of the orthopaedic department. ‘Comprehensive 3-D imaging makes it easier to position implants, screws and osteosynthesis material accurately and also allows much more precise setting of fractures and reconstruction of joint surfaces compared with two-dimensional imaging methods. This enables surgical interventions to be carried out more precisely – particularly for complex intra-articular fracture setting and osteosynthesis in the hip and spinal areas.’
The integration of intra-operative
3-D X-ray imaging and navigation also increases operating room efficiency. Intra-operative monitoring of results enables the number of subsequent corrective interventions and radiological check-ups to be reduced, Ziehm adds. ‘Patients benefit from quicker recovery times and pressure on hospital budgets can be reduced on a continuing basis. For example, a study carried out by the Department of Trauma Surgery at the Hanover Medical School showed that after an intra-operative 3-D scan, repeats are unnecessary in 16 per cent of cases.
‘Because of the many advantages of this equipment, the use of mobile 3-D C-arms has increased in recent years. The consistent refinement of C-arms and the optimisation of image quality with the introduction of flat panel detector technology make them versatile performers in clinical settings such as interventional radiology, vascular surgery or cardiology. Particularly in the case of complex, minimally invasive interventional procedures, both physicians and patients benefit from enhanced spatial orientation and increased precision.’
Source: Ziehm Imaging
30.04.2008